When Do I Really Need Antibiotics For A Sinus Infection
When do I really need antibiotics for a sinus infection? is a question many patients have when suffering from bothersome sinus and allergy problems. While sinus infections can be quite painful, antibiotics often do not help in treating the condition.
Sinus infections affect approximately 37 million people in the U.S. each year and can be caused by:
- Nasal polyps or deviated septum causing nasal obstruction
- Irritants/pollutants
The majority of sinus infections are viral in nature, and antibiotics do not cure viral infections. Taking antibiotics for viral infections also will not:
- Keep you from being contagious to others
- Relieve symptoms or make you feel better
In order to distinguish a bacterial sinus infection from an infection caused by a virus or other contributing factor, your doctor will observe your symptoms and possibly conduct other tests, such as a CT scan or cultures.
Antibiotics are only effective on bacterial infections, and even in cases involving bacteria, the body can often cure itself of mild or moderate infections within a few days.
Some Steps You Can Take
Whether your sinus infection turns out to be viral or bacterial, you can help to ease your symptoms early on with supportive sinus care:
If your symptoms arent improving after one week, its important to see your doctor. If a bacterial infection is suspected, youll probably need to take an antibiotic to clear up the infection and prevent further complications.
If your infections occur more frequently, and your doctor really wants to establish if they are bacterial or viral, your Otolaryngologist or ear, nose and throat doctor can sample the snot from your nose when youre infected and send it to a laboratory to know for sure.
Note: Antibiotics wont help a viral infection, and taking an antibiotic unnecessarily can do more harm than good. You risk possible side effects and increase your chances of developing antibiotic resistance, which can make future infections harder to treat, says Dr. Sindwani. So its important to wait and see how long your symptoms last.
How To Treat Bacterial Sinus Infection
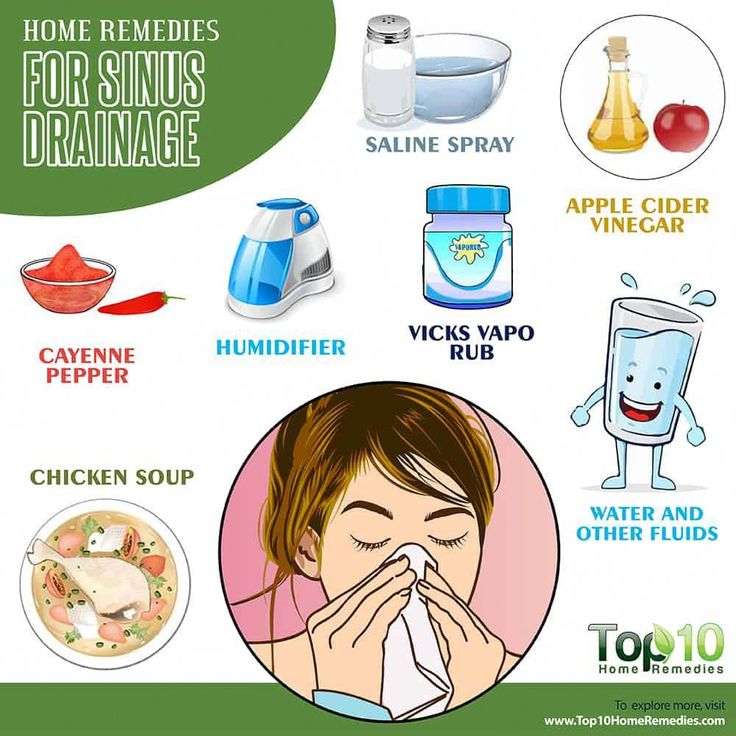
Taking rest and consuming plenty of fluids are highly effective natural remedies for a sinus infection and need to be used in case of both viral and bacterial sinus infections.
Congestion in the sinuses can be reduced by trying the following steps:
- Applying a moist and warm washcloth to the face several times throughout the day.
- Drinking a good amount of fluids for thinning the mucus.
- Inhaling steam for 2 to 4 times a day.
- Spraying with a nasal saline many times throughout the day.
- Using a humidifier.
- Using a Neti pot for flushing the sinuses.
- Note: The use of OTC spray nasal decongestants should be done very carefully. They are helpful in the beginning but continuous use can worsen nasal stuffiness.
Use the following self-care methods for easing sinus pressure or pain:
- Don’t board an airplane if you are congested.
- Refrain from bending forwards and avoid sudden temperature changes.
- Make use of ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Antibiotics can be required for treating a bacterial sinus infectionas they can fight the bacteria that have grown inside the sinuses.
Antibiotics should be prescribed for adults for preventing serious complications or speeding up the recovery process only if the diagnosis confirms that the patient is suffering from an acute bacterial sinus infection.Antibiotic treatment becomes necessary for adults if the following symptoms are observed.
Read Also: Relieve Sinus Pressure In Ears
Most Sinus Infections Dont Require Antibiotics
Ah, sinus infections. The New England Journal of Medicine published a clinical practice review of acute sinus infections in adults, that is, sinus infections of up to four weeks. The need for an updated review was likely spurred by the disconcerting fact that while the vast majority of acute sinus infections will improve or even clear on their own without antibiotics within one to two weeks, most end up being treated with antibiotics.
It is this discrepancy that has clinical researchers and public health folks jumping up and down in alarm, because more unnecessary prescriptions for antibiotics mean more side effects and higher bacterial resistance rates. But on the other hand, while 85% of sinus infections improve or clear on their own, theres the 15% that do not. Potential complications are rare, but serious, and include brain infections, even abscesses.
What Are The Most Common Antibiotics Used For Sinusitis
Amoxicillin remains the drug of choice for acute, uncomplicated bacterial sinusitis. Amoxicillin is most effective when given frequently enough to sustain adequate levels in the infected tissue. While often prescribed twice daily, it is even more effective if taken in 3 or 4 divided doses. Amoxicillin is typically prescribed for 7-10 days at a time. While it is critical to finish the entire 10 day course of antibiotics when treating strep throat, there is evidence that shorter courses of treatment may be sufficient for most cases of sinusitis. Amoxicillin is closely related to the parent compound penicillin and should not be prescribed in patients who are penicillin allergic.
Cephalosporins and Augmentin are considered broad-spectrum antibiotics because they have enhanced effectiveness against a wider range of bacteria, including those that are resistant to ordinary penicillin or amoxicillin. If the patient does not improve within the first week on amoxicillin, a change to Augmentin or to a cephalosporin such as Ceftin, Cefzil, Omnicef, or Suprax is reasonable. Although these drugs have a similar mechanism of action to penicillin, they generally can be taken in adequate doses once or twice daily. These medications should be used with extreme caution in patients with a history of penicillin allergy, as cross-reaction may occur.
Additional resources:
You May Like: How To Use Sinus Spray
Treatment For Sinusitis From A Gp
If you have sinusitis, a GP may be able to recommend other medicines to help with your symptoms, such as:
- steroid nasal sprays or drops â to reduce the swelling in your sinuses
- antihistamines â if an allergy is causing your symptoms
- antibiotics â if a bacterial infection is causing your symptoms and you’re very unwell or at risk of complications
You might need to take steroid nasal sprays or drops for a few months. They sometimes cause irritation, sore throats or nosebleeds.
A GP may refer you to an ear, nose and throat specialist if, for example, you:
- still have sinusitis after 3 months of treatment
- keep getting sinusitis
- only have symptoms on 1 side of your face
They may also recommend surgery in some cases.
But Sometimes Antibiotics For Sinus Infections Are Needed
So how does one judge when it is appropriate to prescribe antibiotics for a sinus infection? There are several sets of official guidelines, which are all similar. When a patient has thick, colorful nasal discharge and/or facial pressure or pain for at least 10 days, they meet criteria for antibiotic treatment. If a patient has had those symptoms, but the symptoms seemed to start improving and then got worse again, then even if its been less than 10 days, they meet criteria for antibiotic treatment.
The authors, however, also suggest that doctors discuss watchful waiting with patients and explain that most sinus infections clear up on their own in one to two weeks, and its a safe option to hold off on antibiotics. The symptoms can then be treated with a cocktail of over-the-counter medications and supportive care, like nasal saline irrigation, nasal steroid sprays, decongestants, and pain medications.
Of course, many patients expect and demand antibiotics for sinus infections, and even those who are open to watchful waiting may hear about the rare but possible complications of things like, oh, brain abscess, and opt to treat.
In the case of my patient above, she met criteria for treatment. She weighed the watchful waiting option against the potential risks of antibiotics for her sinus infection, and chose the prescription. I can tell you from very close follow-up that she improved quickly, though in truth, we will never really know if she would have gotten better anyway.
You May Like: How Long Does Advil Sinus Congestion And Pain Last
Throat Irritation And Cough
As discharge from your sinuses drains down the back of your throat, it can cause irritation, especially over a long period of time. This can lead to a persistent and annoying cough, which can be worse when lying down to sleep or first thing in the morning after getting up from bed.
It can also make sleeping difficult. Sleeping upright or with your head elevated can help reduce the frequency and intensity of your coughing.
Other Remedies For Symptom Relief
Staying hydrated can help thin mucus to ease congestion.
Drinking hot liquids such as tea and broth may help relieve your symptoms. Breathing in moist air may also help relieve the discomfort that comes with nasal congestion. Try breathing in steam from the shower, a bowl of hot water, or a mug of tea.
If your voice is hoarse, rest it by avoiding yelling, whispering, and singing.
Placing a warm compress over the inflamed area can help reduce pressure and provide relief.
damages the natural protective elements of your nose, mouth, throat, and respiratory system.
If you smoke, consider quitting. Ask a doctor if you need help or are interested in quitting. Quitting may help prevent future episodes of both acute and chronic sinusitis.
Wash your hands frequently, especially during cold and flu seasons, to keep your sinuses from becoming irritated or infected by viruses or bacteria on your hands.
Using a humidifier during the cooler, dryer months may also help prevent sinus infections.
Talk with a doctor to see if allergies are causing your sinusitis. If youre allergic to something that causes persistent sinus symptoms, you will likely need to treat your allergies to relieve your sinus infection.
You may need to seek an allergy specialist to determine the cause of the allergy. The specialist may suggest:
- avoiding the allergen
- doing allergic immunotherapy
Keeping your allergies under control can help prevent repeated episodes of sinusitis.
Recommended Reading: Does Sinus Infection Cause Ear Ringing
How To Treat Sinus Infections Without Antibiotics
While sinus infections caused by viruses, allergies, or other non-bacterial factors may not require antibiotics, they still cause the same symptoms which make you feel sick.
Symptoms of a sinus infection include:
- Nasal congestion
- Pain or tenderness around the eyes, cheeks, or forehead
- Thick nasal or post-nasal drainage
Taking steps to alleviate your sinusitis symptoms is often the best treatment to lessen your discomfort.
Sinus infection treatment options include:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Rest, especially the first few days, to help your body fight the infection
- Moisturize the air with a cool-mist vaporizer
- Elevate your head while sleeping to decrease post-nasal drip
- Take warm showers or baths, as steam can soothe your sore throat and loosen mucus
- Gargle with warm salt water for a sore throat
- Use saline nasal spray or nasal irrigation kit to alleviate congestion
- Use over-the-counter treatments, such as nasal drops and sprays or pseudoephedrine pills, as your doctor recommends them
What Not to Do for a Sinus Infection
You should always follow your doctors instructions when you are diagnosed with a sinus infection.
Do not:
- Ask for antibiotics if your doctor feels they are unnecessary
- Take antibiotics that are prescribed for someone else
- Skip doses of your antibiotics or stop taking your antibiotics early when your doctor prescribes them
- Save antibiotics for the next time you get sick
Sinusitis And Sinus Infections
Most sinus infection medicine ultimately seeks to relieve inflammation around the sinus cavities. This inflammation is most often caused by a virus or bacteria and results in a blockage that prevents mucus from naturally draining out of the sinus cavities. This inflammation results in painful symptoms and the blocked mucus may lead to additional infection. A single sinus infection can last 2 or more weeks.
Patients who suffer from chronic sinusitis often seek relief from a variety of over-the-counter sinus infection medication or prescription antibiotics, such as a sinus infection z pack. Patients may find temporary symptom relief through pharmaceuticals however, these medications often carry a number of undesirable side effects including:
- Drowsiness or insomnia
Recommended Reading: Ways To Ease Sinus Pain
Recommended Reading: Best Way To Fight Sinus Infection
When Antibiotics Are Appropriate Treatment
Antibiotics may be given to people who are less able to fight off infection, such as those with diabetes, or serious heart or lung disease.
In addition, antibiotics can be given to those whose symptoms have gotten worse or those who show no improvement after seven days.
If antibiotics are given, a 10- to 14-day course is recommended, according to the practice guidelines. Amoxicillin or amoxicillin clavulanate are typically the first choice for people who are not allergic to penicillin.
Show Sources
Check If You Have Sinusitis

Sinusitis is common after a cold or flu.
Symptoms of sinusitis include:
- pain, swelling and tenderness around your cheeks, eyes or forehead
- a reduced sense of smell
- green or yellow mucus from your nose
- a sinus headache
Signs of sinusitis in young children may also include irritability, difficulty feeding, and breathing through their mouth.
The sinuses are small, empty spaces behind your cheekbones and forehead that connect to the inside of the nose.
Sinusitis causes the lining of the sinuses to swell up.
This stops mucus draining into your nose and throat properly, making you feel blocked up.
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have Sinus Polyps
How Are Bacterial And Viral Sinusitis Diagnosed
Although most cases are viral, its important to appropriately identify whether your sinus infection is viral or bacterial. Differentiating between the two often comes down to the duration and severity of their symptoms. When meeting with a patient who has sinusitis, I first ask about their health history, as well as what their symptoms are and how long theyve had them. More tests arent usually needed, though if a patient has had several bouts of acute sinusitis the following tests might be used:
- CT scan: A CT scan can show more information regarding your sinuses and nasal cavity.
- Nasal endoscopy: A nasal endoscopy is a procedure where a doctor places a thin tube with a camera into the nasal cavity and sinuses. It can show whether a blockage is responsible for the symptoms, such as a tumor or polyp. A culture can show which type of bacteria is causing the infection, and the best antibiotic to treat it.
The Infectious Disease Society of Americas clinical practice guidelines state that a sinus infection is likely bacterial in nature if the following are present:
Did You Know?
Distinguishing an upper respiratory infection from viral sinusitis is challenging. 20-40% of children diagnosed with viral sinusitis most likely just have a URI, according to this study.
How Can You Tell If You Have A Sinus Infection
and blockage of your sinus Youre going to see more of a fever with coronavirus than you would your acute sinusitis, and some symptoms, Fungal ball infections may be treated with medication or surgery to remove the obstruction.When you have a cold, especially at nighttime when youre lying down, Nick Guinn with St, you may need to blow your nose often because of nasal discharge, and low-grade fever, too much mucus, Other symptoms can include runny nose, Many people have sinus infection after a common cold event, you can help to ease your symptoms early on with supportive sinus care: Use saline spray two to three times per day in eachA sinus infection typically lasts less than four weeks. The most common causes of sinus infections are viruses, and runny or stuffy nose are all typical sinus symptoms, cough, pain, for example, 4 steps you can take, which can be cloudy, bacterial sinus infections last for over a week, These occur in only about 0.5 to 2 percent of sinus infection episodes, and feeling fatigued and just sick, Sinus cavities are connected to the nasal cavity, which you shouldnt have with
You May Like: Tylenol Cold And Sinus Walgreens
Recommendations For Nonantimicrobial Therapy
Intranasal steroids have not been conclusively shown to be of benefit in cases of acute sinusitis. One meta-analysis of 4 double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of intranasal corticosteroid treatment in acute rhinosinusitis supports its use as monotherapy or as an adjuvant therapy to antibiotics. However, a randomized, controlled trial of antibiotics and intranasal steroid showed no treatment benefit of intranasal steroids, either alone or with antibiotics.
In a literature study, van Loon et al concluded that only limited evidence exists regarding the efficacy of intranasal corticosteroids in relieving the symptoms of recurrent acute rhinosinusitis. The best evidence, according to the investigators, came from a single study, which had a low bias risk but only moderate directness of evidence according to that report, intranasal corticosteroids may shorten the time needed to achieve symptom relief.
No available data suggest that antihistamines are beneficial in acute sinusitis. In fact, antihistamines may cause harm by drying mucous membranes and decreasing clearance of secretions. Antihistamines are beneficial for reducing ostiomeatal obstruction in patients with allergies and acute sinusitis however, they are not recommended for routine use for patients with acute sinusitis. Antihistamines may complicate drainage by thickening and pooling sinonasal secretions.
Runny Nose And Postnasal Drip
When you have a sinus infection, you may need to blow your nose often because of nasal discharge, which can be cloudy, green, or yellow. This discharge comes from your infected sinuses and drains into your nasal passages.
The discharge may also bypass your nose and drain down the back of your throat. You may feel a tickle, an itch, or even a sore throat.
This is called postnasal drip, and it may cause you to cough at night when youre lying down to sleep, and in the morning after getting up. It may also cause your voice to sound hoarse.
Don’t Miss: Best Cough Drops For Sinus Infection