What Is Sinus Cancer
Cancers occurring in the nasal cavity and the sinuses that branch off of it are rare. Most sinus cancers are squamous cell carcinomas that originate in the lining of the sinuses or nasal cavity. Less common types of sinus and nasal cavity cancers include melanomas and sarcomas . Only about 2,000 people develop any type of nasal or sinus cancer each year in the United States .
Many of the symptoms of sinus cancer resemble those of inflammation or infection of the sinuses , such as congestion, postnasal drip, , pain under the eyes or above the eyebrows, and earache or toothache. Nosebleeds and can also occur. Unlike the symptoms of inflammation and infection, the symptoms of sinus cancer do not improve.
Treatment of sinus depends upon the type of cancer present, where it is located, its size, whether it has spread, and your overall health status. Surgery is often part of treatment, and may be preceded or followed by or chemotherapy.
Complications of sinus cancer requiring emergency care are rare. Seek immediate medical care for a nosebleed that will not stop or extremely severe . Seek prompt medical care if you have symptoms of that persist for more than a couple weeks get frequent bloody noses develop double vision, facial , or a change in facial appearance or have other symptoms that concern you.
Types Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancers
Cancer can start from any type of cell that makes up the mucosa, and each type of cancer acts and grows differently.
Each of these types of cancer has a distinct behavior and outlook. They cannot all be treated the same way. Many of them rarely affect the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, so they’ve been hard to study. Because of this, doctors must base treatment decisions on their experience with similar cancers in other parts of the head and neck.
Different Types Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer
The nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses are lined by a layer of mucus-producing tissue . The mucosa has many different types of cells that include squamous cells, glandular cells, nerve cells, and infection-fighting cells. Cancer can start from any of these cells.
- The most common type of nasal cavity or paranasal sinus cancer is called squamous cell carcinoma .
- Other less common types are adenocarcinoma
- Esthesioneuroblastoma
- Lymphoma
Read Also: What Prescription Medicine For Sinus Infection
Common Treatments For Sinus Cancer
Options for treating sinus cancer include:
-
to attack cancer cells
-
Participation in a clinical trial that is testing promising new therapies and treatments for sinus cancer
-
Radiation therapy to attack cancer cells
-
Surgery to reconstruct areas that needed to be removed to treat the cancer
-
Surgery to remove the cancer and evaluate how far it has spread
What Are Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancers
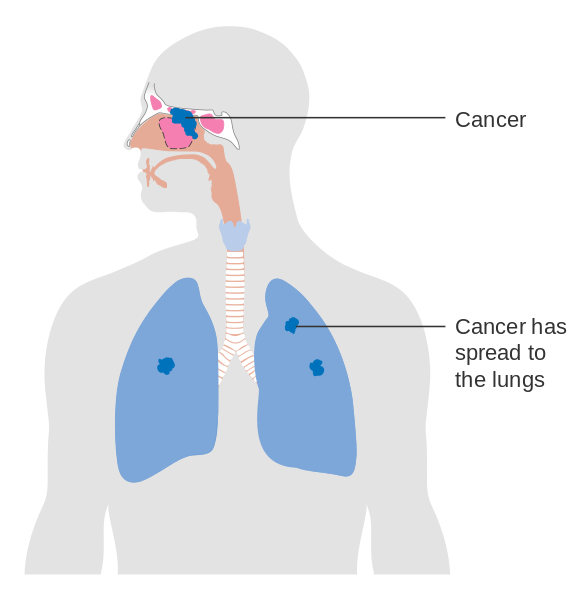
Nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers start in the head and neck area. Cancer that starts in the nasal cavity is called nasal cavity cancer. Cancer that starts in the paranasal sinuses is called paranasal sinus cancer. These cancers start when cells in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinus grow out of control and crowd out normal cells.
Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the nasal cavity or paranasal sinus area can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or bones, and grow there. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis and the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from where it started. When nasal cavity or paranasal sinus cancer spreads, its still called nasal cavity or parasinus sinus cancer. Its not called lung cancer unless it starts from cells in the lung.
The information after the pictures below is about nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers.
Ask your doctor to use these pictures to show you where the cancer is.
The nasal cavity
Explore the 3D interactive color model to learn more.
Don’t Miss: Who To See For Sinus Issues
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- Where the tumor is in the paranasal sinus or nasal cavity and whether it has spread.
- The size of the tumor.
- The type of cancer.
- The patient’s age and general health.
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred .
Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancers often have spread by the time they are diagnosed and are hard to cure. After treatment, a lifetime of frequent and careful follow-up is important because there is an increased risk of developing a second kind of cancer in the head or neck.
What You Should Know About Sinus Cancer And Nose Cancer
Cancers of the nose and sinuses account for less than 1% of all tumors, but the nose and sinus give rise to a greater variety of tumors than any other site in the body. In fact, there are hundreds of types of tumors that can arise in the nose and sinuses. The most common are:
- squamous cell carcinoma
- adenocarcinoma
- esthesioneuroblastoma and sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
Other nose and sinus cancers include neuroendocrine carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, melanoma and all types of sarcomas.
To learn more about nose cancer and sinus cancer, we spoke with Shirley Su, M.D., assistant professor in Head and Neck Surgery. Here’s what she had to say.
What are common symptoms or nose cancer and sinus cancer?New onset of blocked nose, frequent nose bleeds, loss of sense of smell, change in vision or double vision, swelling of the face or eye, headaches and numbness of the face.
These tumors also may not present symptoms and may be found during sinus surgery or on CT scans for an unrelated complaint.
How are these cancers typically diagnosed?Diagnosis requires a biopsy and having the specimen examined by a pathologist. Having an experienced pathologist look at the biopsy is critical. There are so many different types of tumors in this region, and treatment can be completely different for two tumors that look very similar under the microscope.
Why are nose and sinus cancers typically hard to treat?Coming to the correct diagnosis is the first hurdle.
Also Check: The Best Sinus Infection Medicine
About Sinus And Nasal Cancers And Types
Sinus cancer, nasal cancer and skull-base cancer usually originate in the maxillary sinus, the nasal cavity, and the ethmoid sinus, in that order. Cancers that originate at the top of your maxillary sinus, located between the eyes and the upper jaw, can invade your eyes and affect your vision. Those that invade through the back wall can access the nerves and vessels at the base of your skull and move directly into your brain. Those tumors represent extremely advanced disease.
Tumors arising in the ethmoid sinus, between the eye sockets and the nose, and the nasal cavity can also spread to an eye or the optic nerve. They can also invade the thin bone at the base of your skull and spread within your brain.
What Is Nasal Cancer
The nose and sinuses that surround the nasal cavity may in rare circumstances develop cancer. The nasal cavity is defined by the area within the nose, excluding the skin whereas the sinuses are collectively known as the paranasal sinuses and include: the maxillary sinuses, ethmoid sinuses, sphenoid sinuses, and the frontal sinuses. The sinuses are air filled pockets of bone that sometimes can harbor both malignant and benign tumors. Most often, growths within the nasal and paranasal sinuses are benign. However, the most common malignant tumor is squamous cell carcinoma, usually occurring in the maxillary sinus.
Also Check: Does Ibuprofen Help With Sinus Headache
Types Of Nasal Cavity And Sinus Cancers
The type of nasal cavity or sinus tumor you have is determined by how cells taken from the tumor look under a microscope. These cells are collected during a biopsy.
The most common type of nasal cavity or sinus cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells are the thin, flat cells that make up the lining of the nasal and sinus passages.
Other examples of cancerous tumor types include salivary gland cancer, sarcoma, esthesioneuroblastoma, lymphoma, sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, and melanoma.
Examples of noncancerous nasal cavity and sinus tumors include squamous papilloma, inverted papilloma, and adenoma.
Determining the type of nasal cavity or sinus cancer helps doctors predict how the disease will respond to specific treatments. This way we can personalize your treatment.
Treatment Of Stage Iv Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- External radiation therapy and/or internal radiation therapy with or without surgery.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy before surgery or radiation therapy.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy after surgery or other cancer treatment.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: How To Heal A Sinus Infection Without Antibiotics
Tests That Examine The Sinuses And Nasal Cavity Are Used To Diagnose Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity Cancer
The following tests and procedures may be used:
Diagnosis Of Nasal Cavity And Sinus Cancers
A biopsy is the first step in the diagnosis of nasal cavity or sinus cancer. During a biopsy, a small amount of the tumor is removed. A pathologist then examines the sample to determine what type of tumor you have.
Special X-rays, such as CT scans, MRIs, or PET/CT scans, may provide more details about how deep the cancer is and if it has spread.
The information from your biopsy and imaging scans allows your doctor to tell you the stage of the cancer. The stage measures how widespread or advanced the cancer is. It guides the recommendations for your treatment.
You May Like: Can You Heal A Sinus Infection Without Antibiotics
How Is Nasal Cancer Diagnosed
In addition to routine history and physical examination, the physician may perform ancillary tests and procedures in order to confirm the presence and type of sinonasal cancer, as well as to determine the presence of second primary cancers or the spread of malignant disease elsewhere.
Treatment For Metastatic Throat Cancer
As with other cancers, the sooner throat cancer is detected, the easier it is to treat and the better the chances are of the treatment being successful. When throat cancer has metastasized to distant structures like the lungs or bones, it is considered advanced or late-stage cancer, and treatment will likely involve multiple approaches.
Moffitt Cancer Center is dedicated to providing patients with any stage of throat cancer with the best possible treatment and care. The specialists within our Head and Neck Cancer Program take an individualized approach to treatment, giving our patients the best chance of a positive outcome and an improved quality of life. If you would like to learn more about receiving metastatic throat cancer treatment at Moffitt, fill out a new patient registration form online or call .
- BROWSE
Also Check: What Is The Best Sinus And Allergy Medicine
Diagnosis Of Sinus Cancer
First, youll meet with your doctor for a physical exam. If your doctor finds possible signs of sinus cancer, they will order more tests, including:
- Imaging tests: Scans including CT, MRI, PET scans and X-rays help confirm if a tumor exists and if its spread to other areas.
- Sinus endoscopy: A thin, lighted tube is inserted into the nose. This allows your doctor to look for possible abnormal tissue inside your sinuses.
- Biopsy: The removal of a small piece of tissue thats suspected of being cancerous.
How Common Are Sinus Tumors
Cancers of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses are rare, with about 2,000 people in the United States developing these cancers each year. These tumors are more common with age, with about 4 out of 5 cases occurring in people who are at least 55 years old. Men are more likely than women to get these cancers.
What does a CT scan of sinuses reveal?
Sinus CT scanning is used for the following purposes: to assess fluid-filled or thick-membraned sinuses. to help confirm a sinusitis diagnosis. to assess disorders that cause inflammation. to learn about growths in the nasal cavity and sinuses .
You May Like: Where To Get Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
Outlook For Nasal And Sinus Cancer
There are many different types of cancer that can affect the nasal cavity and sinuses.
The outlook varies, depending on the specific type of nasal and sinus cancer you have, its exact location, how far it’s spread before being diagnosed and treated, and your overall level of health and fitness.
The Cancer Research UK website has more information about the outlook for nasal and sinus cancer.
Staging And Grading Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancers
Cancer can develop in the nasal cavity or any of the several pairs of sinuses. The cancer may then spread to nearby tissue, the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
The staging of nasal and paranasal sinus cancers is complex. The staging systems are only for maxillary sinus, ethmoid sinus and nasal cavity cancer.
For a cancer anywhere else in the sinuses your doctor will decide on your treatment differently. They will look at the size, location and type of the tumour you have.
-
V Paleri and N Roland
The Journal of Laryngology and Otology, volume 130, number S2, May 2016
-
Cancer and its management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley-Blackwell, 2015
Recommended Reading: Aleve D Sinus And Headache Discontinued
Expert Review And References
- Carrau RL. Malignant Tumors of the Nasal Cavity. WebMD LLC 2011: .
- Cancer of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinus: radiation therapy and chemotherapy management. Harrison LB, Sessions RB, & Kies MS. Head and Neck Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2014: 21: 560-587.
- Mendenhall WM, Werning JW, Pfister DG. Cancer of the head and neck. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, & Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 38: 422-473.
- Runbin P, Hansen JT. TNM Staging Atlas with Oncoanatomy. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2012: .
- Tabaee A, Persky MS. Cancer of the nasal vestibule, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, anterior skull base, and orbit: Surgical management. Harrison LB, Sessions RB, & Kies MS. Head and Neck Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2014: 20:525-559.
After Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Paranasal Sinuses And Nasal Cavity Or To Other Parts Of The Body
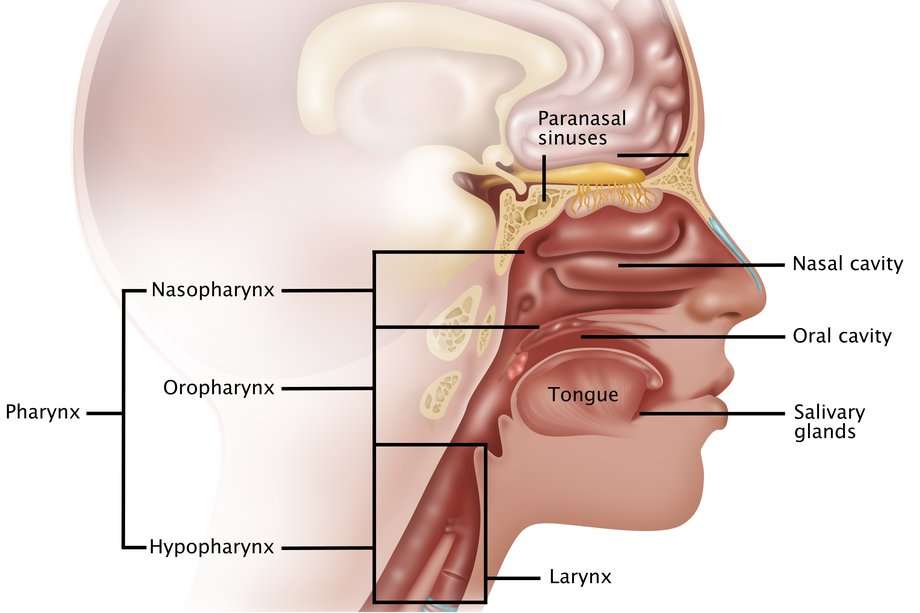
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
You May Like: Will Z Pack Treat A Sinus Infection
Further Tests For Nasal And Sinus Cancer
These tests may be used to help diagnose nasal and sinus cancer or to check whether it has spread.
- X-rays
X-rays are used to take pictures of the inside of your body. It is not painful and only takes a few minutes.
- CT scan
A CT scan uses x-rays to build a three-dimensional picture of the inside of the body.
- MRI scan