Is Removing A Cyst Painful
If you’ve never had a cyst removed before, don’t worry the procedure is typically fast and painless. The steps of cyst removal typically involve: Numbing The doctor will use a lidocaine injection to numb the area. Removal The sac containing the fatty tissue and fluid are removed using a sharp instrument.
Which Of These Possibilities Are Unlikely Explain Why
A mucous retention cyst is the most likely nonneoplastic, salivary glandrelated cause, and the bluish tinge to the lesion suggests a cyst. However, this lump is firm and appears to be of long duration. A mucous retention cyst would be expected to burst or fluctuate in size if present over a long period. This lesion is rather large for a mucocoele on the palate.
Antral or nasal causes must be borne in mind but are also unlikely. Any lesion that had eroded through the palate or sinus wall would be expected to be ulcerated or inflamed.
Sumit Samant, , in, 2021
What Drugs Are Used To Treat Sinus Cysts:
- Vasoconstrictor agents. They help to normalize the human respiratory system and remove swelling
- Antihistamines. They are used if the swelling is caused by an allergic reaction
- Mucolytic drugs. They normalize the outflow of mucus
- Antiseptic. They help fight inflammation and clean the mucous surface of the nasopharynx
- Nasal sprays and drops. Medications help normalize the flora
- Painkillers. It is necessary for strong pressure and pain due to sinus cyst.
Donât Miss: How To Get Rid Of Sinus Pain In Face
Recommended Reading: How To Clear A Clogged Ear Due To Sinus Congestion
Alternative Treatment Of The Sinus Sinus Cyst
Alternative treatment of the cyst of the maxillary sinus, oddly enough, may cause an increase in cystic education and worsen overall well-being. In addition, there are often cases of exacerbation or the emergence of allergies to certain herbs or other plant components.
Basically, the alternative formulation is based on the use of herbs and biologically active substances, which are contained in propolis or honey. Unfortunately, such recipes rarely lead to complete cessation. Neither instillation of the nose with broths, nor washing or inhalation, nor taking various preparations made at home with plant ingredients, will not help get rid of the cyst. Also, doctors strongly recommend that you stop taking homeopathic medicines and go through various homeopathic procedures.
, , , , , , ,
Read Also: How To Relieve Severe Sinus Headache
Mucosal Thickening Of Maxillary Sinus
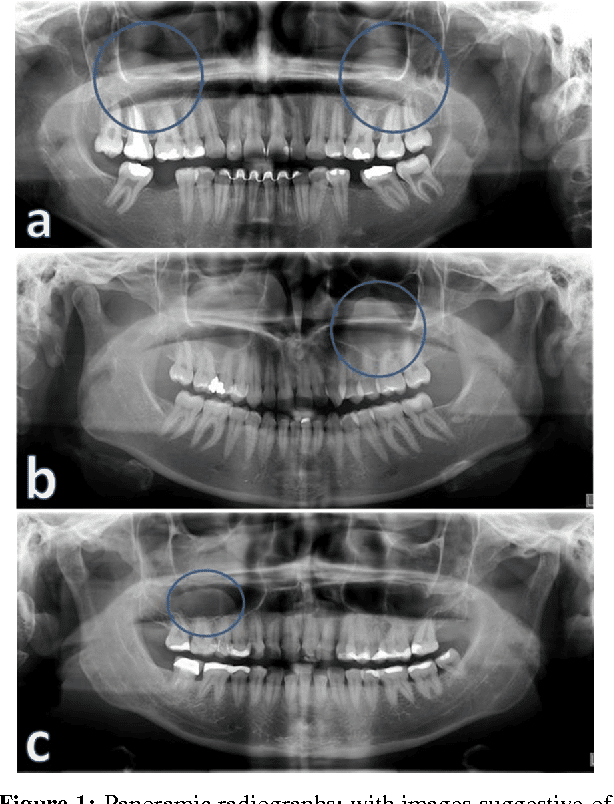
Mucosal thickening of maxillary sinus
Mucosal Thickening Of Maxillary Sinus. Mucosal thickening is an inflammatory reaction with hyperplasia of the mucous lining of the maxillary sinus. It means that the disease process has begun in the sinuses. However, the nature of the spatial relationship between the maxillary sinus floor and the infected root tips or between the sinus floor and periapical lesions. If severe, sinusitis can cause frequent/vacuum headaches.
Maxillary Sinus Mucosal Thickening Due To Foreign Body | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org From radiopaedia.org
Sphenoid sinus mucosal thickening in pituitary apoplexy etiology, there are reports on the appearance of sphenoid sinus mucosal thickening 1) 2). I have treatment planned a bilateral external sinus lift on a patient. Make sure you discuss your specific case with your treating physician. Sinusitis is an inflammation, thickening, and swelling of the normal tissue called mucosa, which lines all the sinuses, their channels to the nose and the nose itself. Thickening of the mucosa of the paranasal sinuses is a common occurrence. Signal characteristics of the affected regions include.
Also Check: Where Does Sinus Cancer Spread To
Chronic Rhinosinusitis And Complications
An underlying odontogenic infection is reported to be the cause in up to 40% of chronic rhinosinusitis . In addition, several other conditions may mimic rhinosinusitis and challenge the radiological interpretation.
Five distinct radiological inflammatory patterns have been described, each with a different therapeutic course and surgical options , where the first three are caused by obstruction of the mucociliary flow. Obstruction of the maxillary sinus drainage is the most common. The level of obstruction is at the ostium and the thin ethmoid infundibulum and referred to as infundibular pattern. Obstruction of the middle meatus, the common drainage way for the frontal, anterior ethmoid, and maxillary sinuses, will cause obstruction of ipsilateral sinuses and is referred to as ostiomeatal complex pattern. Less common is obstruction of the sphenoethmoidal recess that drains the posterior ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses. The two last patterns are sinonasal polyposis and incidental findings.
Complications to CRS are bone thickening , demineralization and erosion of bone, and a negative sinus pressure that can cause infoldings of the sinus walls, referred to as silent sinus syndrome , which may result in larger orbit and cause enophthalmos and diplopia.
Hypoplastic maxillary sinus with retracted posterior fontanelle may mimic silent sinus syndrome but usually has no clinical impact despite the mucus-filled sinus .
Figure 8.
Advantages Of The Endoscopic Sinus Cyst Removal Method:
- Local anesthesia
- The possibility of application in the field of pediatrics
- Reduced likelihood of recurrence of cysts
- Hospital stay up to 2 days
- Due to the use of a small video camera, the accuracy of the surgeons actions increases
- Fast healing process. The operation does not leave scars, there is no risk of adhesions
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Symptoms Of Sinus Problems
How To Avoid Maxillary Cysts
Simple prevention measures help to avoid the appearance of the cysts:
Monitor the immunity system, try not to catch a cold. In cold weather abstain from swimming pools and sports activities in the fresh air.
Do not let a disease take its course. It is viral diseases that become the main cause of chronic sinusitis, and after them the cyst. If there is anything similar to maxillary retention cysts symptomatic, the doctor should be visited.
Visit your dentist regularly. Sometimes inflammation from the roots of the teeth spreads to the sinuses.
After the treatment, the cyst can recur. To prevent relapse, regularly see an otolaryngologist. Find out whats causing the problem.
And remember, any pathology should be treated by the doctor. Self-treatment, even natural, is ineffective and has serious consequences without the specialist control.
Maxillary Sinus Mucous Retention Cyst Treatment
Some of the simple treatment options for the effective management of maxillary sinus cyst include,
- Nasal Irrigation: Nasal irrigation is considered to be beneficial in the management of almost all types of sinus ailments. Take a cup of water and add a few a teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate to it. Now using a plastic syringe, inject the solution into the right nostril, so as to allow them to pass through the nasal passages and then come out through the left nostril. Ensure that the water is lukewarm. Repeated the same with the other nostril.
- Steam Inhalation is also considered beneficial. The vapors of the steam help in decongestion of the maxillary sinus and provide instant relief in cases of sinus infection or obstruction. Further it improves the circulation of blood, which in turn hastens thinning and expulsion of the mucus from the sinus
- Garlic tea is considered very beneficial. Garlic has strong anti bacterial and anti microbial properties which makes it very useful in the management of sinus infections. Drink a tea comprising of a couple of crushed cloves of garlic about twice a day. Alternatively inhaling the steam of boiling water containing a few cloves of garlic can also provide relief.
- Apple cider vinegar is also as beneficial in the management of sinus infection as garlic. It can be used along with steam inhalation or a few drops can be added to the water used to nasal irrigation. Diluted vinegar can also be consumed internally.
Also Check: What’s The Difference In Sinus And Allergies
Types And Treatments Of Mucous Retention Cysts
Mucous retention cysts can be scary. Many people develop them somewhere in the upper respiratory tract and fear it may be cancerous. They are actually benign, but can cause blockages and/or pain. They are often associated with chronic sinusitis, seasonal allergies, or strain on the vocal chords. This article will help you understand the different types of these cysts, what causes each type and treatment options.
Are Maxillary Mucosal Cysts A Manifestation Of Inflammatory Sinus Disease
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 January 2007
- Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital, London, UK.
- N K Chadha
- Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital, London, UK.
- G Rogers
- Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital, London, UK.
- *
- Address for correspondence: Mr R P S Harar, 2 The Boulevard, Manor Rd, Woodford Green IG8 8GW
Also Check: Treat Sinus Headache At Home
Maxillary Sinus Retention Cysts Symptomatic And Causes
by Anna Lopez· April 26, 2019
Retention cyst is one of the cyst kinds that are classified according to their structure. Its peculiarity and main difference from so-called pseudocystsis that it is formed as a result of the mucus duct blockage. Given that all the walls are formed by the mucous membrane that contain the glands in large quantities, cysts can be multiple and on the any sinus walls.
While the second kind, which is a pseudocyst does not have a typical internal lining of the mucous membrane. It can be made of other types of tissues. Inflammatory fluid in cysts of this type is considered to accumulate due to inflammation of the upper jaw teeth. That is why pseudocyst cysts are located on the lower part of the maxillary sinus.
These two subspecies of the maxillary sinus cyst can be quite difficult to distinguish from each other in clinical and radiological picture. But this does not change the tactics of treatment.
Maxillary Sinus Retention Cysts Symptomatic
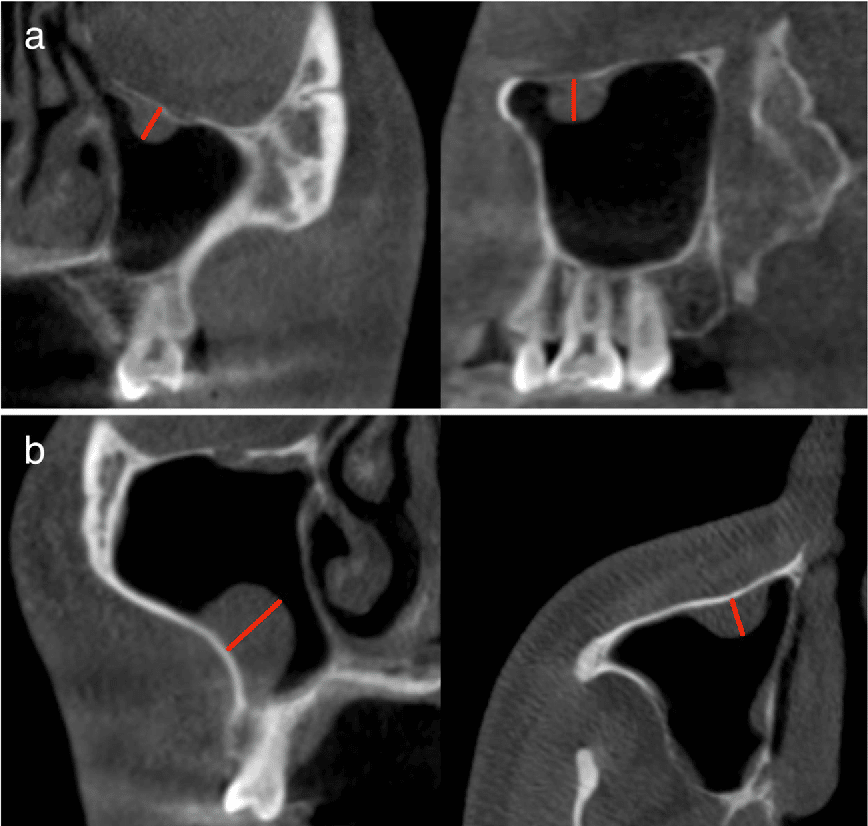
Maxillary sinus retention cysts symptomatic is almost the same as the other cysts kinds and express the same way.
Its manifestations, especially at the initial stages of development, are practically absent. That is why it is always difficult to separate complaints directly related to the cyst from complaints related to other pathologies of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
As usual, the disease is detected when the cyst reaches a significant size and accordingly clinical manifestations of maxillary retention sinus cysts symptomatic appear. Or it is detected accidentally, when doing skull bones radiography procedure for some other reasons.
However, there is a number of symptoms that allow to notice it:
- onstant runny nose
- pain in the projection of the maxillary sinus, especially when press or tilt
- difficulty in nasal breathing
- smell loss
The doctor conducts the persons examination and sends him to the x-ray screening. In addition, MRI or CT examination may be prescribed. To determine the nature of the cyst, they take a puncture of its content and send it to the histology.
You May Like: How To Unclog Ears With Sinus Infection
Innervation Of The Maxilla And Of The Maxillary Teeth
The nervus trigeminus is a mixed nerve responsible for sensation in the face and certain motor functions, such as biting and chewing. It has three major branches: the n. ophthalmicus, n. maxillaris, and the n. mandibularis. The n. ophthalmicus and n. maxillaris are purely sensory. The n. mandibularis has both sensory and motor functions .
Figure 2.
Figure 3.
N.infraorbitalis, c. infraorbitalis and f.infraorbitalis
The n. alveolares superiores arises from the n. maxillaris in the fossa pterygopalatina just before n. infraorbitalis enters the orbita or arises from the n. infraorbitalis in the sulcus infraorbitalis. The upper alveolar nerves are divided in three groups: the n. alveolaris superior posterior, the n. alveolaris superior medius, and the n. alveolaris superior anterior. Working 5 mm above the roots of the teeth in the maxilla will avoid damage to the neurovascular plexus. This is one of the most important points during surgical procedures performed in the maxillary sinuses when the teeth are vital . A second important point is to avoid damage to the n. infraorbitalis, which is commonly damaged during elevation and retraction of mucoperiosteal flaps.
Figure 4.
N. infraorbitalis, c. infraorbitalis and f. infraorbitalis .
Causes Of The Cysts Of The Maxillary Sinus
What are the main reasons for the appearance of the cyst of the maxillary sinus? Most often, these are chronic diseases such as rhinitis or sinusitis, which develop in the nose or paranasal sinuses. However, it happens that the cyst of the maxillary sinus appears and not because of this. The main mechanism and cause of development of the maxillary sinus cyst is a thickening, due to a variety of inflammatory processes, the mucous membrane in the nasal cavity and sinuses, which leads to the fact that the channels that remove mucus from the glands are clogged, overgrown and can no longer remove it. Because the mucus gradually accumulates, which leads to the appearance of mucous balls.
Read Also: Sinus Surgery Cost Without Insurance
Acute Rhinosinusitis And Complications
Acute rhinosinusitis , defined as symptoms less than 4 weeks, is the most common disease of the paranasal sinuses. Fluid is often an incidental finding at CT and should not be misinterpreted as ARS. Mucosal thickening and air bubbles in the opacification can be interpreted as ARS, if clinical symptoms harmonize .
Figure 5.
Coronal CT shows right-sided maxillary opacification with air bubbles consistent with acute rhinosinusitis. Coronal CT shows thick, sclerotic right maxillary sinus walls that indicate a long-standing infection. In addition, the sinus walls are retracted due to a vacuum effect, referred to as sinus silent syndrome. In the left maxillary sinus, the opacification contains air bubbles consistent with an active bacterial infection.
In acute rhinosinusitis, imaging is only indicated when complications are suspected. Extra-sinonasal spread of infection is rare but needs urgent treatment. Children are at most risk. Intraorbital spread from ethmoid and frontal ARS is the most common complication and may present as cellulitis, subperiosteal or intraorbital phlegmon and abscess, and lateral displacement of the medial rectus muscle . The clinical presentation may be forward protrusion of the eyeball, proptosis .
Figure 6.
Intracranial spread is most commonly seen in frontal and ethmoid ARS and presents as complications that include epidural and brain abscesses, subdural empyema, meningitis, and cavernous sinus thrombosis .
Figure 7.
Polyp In Right Maxillary Sinus
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Sinus Infection
Read Also: Allergy Asthma And Sinus Center Warner Robins Ga
What Is Dangerous Cyst Maxillary Sinus
What can happen, get an adult man in his body cyst maxillary sinus? As described above if the cyst is small, imperceptible and insignificant, there will be no special harm from it, although it can roll in your body all your life. However, with a more impressive size of the slime collector and even with inflammation or decay, such a disease can threaten you with increased pressure on the internal organs of the head, an increase in body temperature, and in very neglected cases in general the transition of inflammation to neighboring tissues and organs.
At the worst outcome, the cyst can burst, which will result in the release of a purulent fluid from it, which will not only create discomfort, but can lead to infection of tissues, and then necrosis.
, , , , , , ,
Is Sinus Surgery For Nasal Polyps Worth Getting
Endoscopic sinus surgery with polypectomy has been shown to be one of the most effective treatments for nasal polyps. It reduces symptoms dramatically, and people suffering for years with nasal congestion and smell loss will tell you that sinus surgery has greatly improved the quality of their life. Make an appointmentwith Dr. Thomas Higgins today if want to know more about nasal polyps and if sinus surgery is indicated for you.
Read Also: Best Antibiotic For Acute Sinus Infection
Maxillary Sinus Cyst Symptoms: Mucous Retention Cyst Treatment
The maxillary sinus is located on either side of the face just behind the cheekbones. These sinuses play an important role in drainage of the nasal discharges. Occasionally, cystic growths comprising of small pocket like structures filled in air, semi-solid or liquid material, obstruct the passage of nasal discharges through the sinus and are associated with pain and nasal congestion.
Maxillary sinus cysts can be managed effectively using simple home remedies, since in most cases, maxillary sinus cysts are benign in nature.
Also Check: Best Antibiotic For Acute Sinus Infection
How Is Maxillary Sinusitis Diagnosed
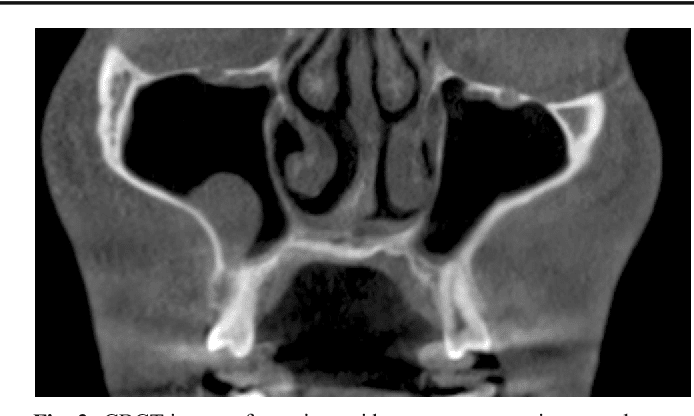
Infection of the maxillary sinuses are usually related to problems with drainage. This may be caused by an obstruction, inflammation, polyps, a deviated septum, or abnormally thick mucus caused by a virus. Maxillary sinusitis can even be caused by dental disease, and is sometimes first diagnosed by a dentist. Learn more about sinus pressure in the teeth, and the relationship between a tooth infection and a sinus infection.
Symptoms may include:
- Postnasal drip
During an exam, the doctor may tap along your cheeks, teeth, or gums to see if you have tenderness, pain or swelling. Your doctor may order a CT scan or other tests to confirm a diagnosis.
Read Also: Get Antibiotics For Sinus Infection Online
The Mucosal Retention Cyst Of The Maxillary Sinus: Case Report
The mucosal retention cyst of the maxillary sinus is a pathologic cavity filled with mucus. Clinically, the retention cyst is asymptomatic, and when symptomatic may come along with headache and facial neuralgia. A 49-year-old patient sought the University Dentistry Department. The patient presented facial asymmetry on intraoral examination, we found an expansive lesion in the fundus of the right maxilla, located in the region between dental units 14 and 17. Slow progression, painful symptoms, and discomfort when placing the prosthesis. The tomography revealed a hyperdense image inside the right maxillary sinus. The patient underwent an incisional biopsy and the histopathological diagnosis was of mucous retention cyst. The lesion was marsupialized for 9 months and was subsequently submitted to surgical enucleation of the lesion, followed by curettage of the bone wrapper. The patient progressed well and presents herself in follow-up.
- Previous article in issue