Sinusitis : Antimicrobial Prescribing
People presenting with symptoms for around 10 days or less
1.1.1 Do not offer an antibiotic prescription.
1.1.2 Give advice about:
-
the usual course of acute sinusitis
-
an antibiotic not being needed
-
managing symptoms, including fever, with self-care
-
seeking medical help if symptoms worsen rapidly or significantly, do not improve after 3 weeks, or they become systemically very unwell.
1.1.3 Reassess if symptoms worsen rapidly or significantly, taking account of:
-
alternative diagnoses such as a dental infection
-
any symptoms or signs suggesting a more serious illness or condition.
For a short explanation of why the committee made these recommendations, see the evidence and committee discussion on no antibiotic.
Full details of the evidence and committee discussion are in the evidence review.
People presenting with symptoms for around 10 days or more with no improvement
1.1.4 Consider prescribing a high-dose nasal corticosteroid for 14 days for adults and children aged 12 years and over, being aware that nasal corticosteroids:
-
may improve symptoms but are not likely to affect how long they last
-
could cause systemic effects, particularly in people already taking another corticosteroid
-
may be difficult for people to use correctly.High-dose nasal corticosteroids used in the studies were mometasone 200 micrograms twice a day and fluticasone 110 micrograms twice a day. This is an off-label use of nasal corticosteroids See NICE’s information on prescribing medicines.
How Is Acute Sinusitis Diagnosed
Your doctor can usually diagnose acute sinusitis from listening to your typical symptoms. They may also check to see if you have a temperature or if you have tenderness over your sinuses. They may examine your nose, as often the lining of the nose is swollen in acute sinusitis. Investigations are not usually needed to diagnose acute sinusitis. Occasionally, blood tests, X-rays or scans are advised if the diagnosis is not clear.
Get The Best Antibiotics For Sinusitis Infection
Antibiotics are used to medicate sinus infections, whether acute or chronic sinusitis. The difference is in the dosage. Since acute sinus infections inflict a person for a short period of time only, the antibiotic dosage is commonly just one round of seven days. Dosage for chronic infections may take several weeks, and is likely to repeat throughout the year.
While you can get some antibiotics over the counter, it is best to get checked up by your doctor first and get a prescription.
Survey Says
A survey conducted on the usage of the antibiotics for sinusitis shows that many take antibiotics from the penicillin family. Macrolides and cephalosporins come next.
Amoxicillin
If the number of users is an indication, then Amoxicillin is probably the best antibiotics for sinus infection. It belongs to the penicillin family.
Amoxicillin works by affecting the metabolism of bacteria. It slows it down, alongside increasing the production of your bodys enzymes. Eventually, the bacteria weakens and is killed off.
Studies peg the effectiveness of Amoxillin in curing sinus infections at almost 89%. This is for acute sinusitis only. Chronic ones may experience different levels of effectiveness.
Amoxicillin should be taken every 8 hours or 12 hours, at 250 milligrams or 500 milligrams respectively. Children are given less dosage, depending on their weight and age.
The drug is available in tablet, liquid and chewable tablet forms. It doesnt matter if youve eaten when you take it.
Read Also: Louisiana Ear Nose Throat And Sinus
What Are The Most Common Antibiotics Used For Sinusitis
Amoxicillin remains the drug of choice for acute, uncomplicated bacterial sinusitis. Amoxicillin is most effective when given frequently enough to sustain adequate levels in the infected tissue. While often prescribed twice daily, it is even more effective if taken in 3 or 4 divided doses. Amoxicillin is typically prescribed for 7-10 days at a time. While it is critical to finish the entire 10 day course of antibiotics when treating strep throat, there is evidence that shorter courses of treatment may be sufficient for most cases of sinusitis. Amoxicillin is closely related to the parent compound penicillin and should not be prescribed in patients who are penicillin allergic.
Cephalosporins and Augmentin are considered broad-spectrum antibiotics because they have enhanced effectiveness against a wider range of bacteria, including those that are resistant to ordinary penicillin or amoxicillin. If the patient does not improve within the first week on amoxicillin, a change to Augmentin or to a cephalosporin such as Ceftin, Cefzil, Omnicef, or Suprax is reasonable. Although these drugs have a similar mechanism of action to penicillin, they generally can be taken in adequate doses once or twice daily. These medications should be used with extreme caution in patients with a history of penicillin allergy, as cross-reaction may occur.
Additional resources:
Which Types Of Doctors Treat Sinusitis And Sinus Infections

- Many sinus infections can be treated by your primary care physician or an Internal Medicine doctor.
- However, it is not unusual to consult an ENT specialist,
- Infectious disease specialist,
- Allergist or Immunologist.
Recommended Reading: Can Sinus Pressure Make You Dizzy
What Is Sinus Infection
Medically known as rhinosinusitis, Sinus infection or Sinusitis is an inflammation or swelling of the tissue lining the sinuses. Healthy sinuses are filled with air. But when they become blocked and filled with fluid, germs can grow and cause an infection. It occurs when your nasal cavities become infected, swollen, and inflamed. Sinusitis is usually caused by a virus and often persists even after other upper respiratory symptoms are gone. In some cases, bacteria, or rarely fungus, may cause a sinus infection.
Vicks Dayquil Cough Cold And Flu Relief
Vicks DayQuil Cough Cold and Flu Relief are softgels that contains acetaminophen which has been widely used as a pain reliever or fever reducer, dextromethorphan which is an effective cough Suppressant, phenylephrine which is a nasal decongestant. Following the main ingredients, this over-the-counter medicine also has povidone and guaifenesin one has an antibacterial property and the latter is an expectorant that helps clear mucus and phlegm from the chest.
Proven effective in relieving fever, headache, nasal congestion, sinus congestion, sore throat, cough and flu-like symptoms such as minor body aches and pains. Taking this on daytime is not a problem since, unlike the commonly used drugs for colds, Vicks DayQuil Cough Cold and Flu Relief has a non-drowsy formula. To achieve the best effect, take two caplets every four hours. Be mindful that taking this medication should not exceed more than 5 days especially if symptoms get worse. It is still advisable that incase symptoms worsen, please consult a doctor.
Pros
Recommended Reading: Best Medicine For Sinus Cold And Cough
When Should You Use Antibiotics
You usually need an antibiotic when you have an infection that is caused by bacteria, and the infection is not going away on its own. This may be the case when:
- Your symptoms last more than 10 days.
- Your symptoms start to get better, but then get worse again.
- Your symptoms are very severe. You should get immediate treatment if:
- You have severe pain and tenderness in the area around your nose and eyes.
- You have signs of a skin infectionsuch as a hot, red rash that spreads quickly.
- You have a fever over 102°F.
Pathogenesis Of Acute Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis usually follows an acute upper respiratory tract infection . As the viral infection spreads in the nasal mucosa, swelling and oedema of the mucosa results. As the mucosal surfaces of the ostiomeatal unit are in close proximity to one another , obstruction of the sinus ostia results. In addition, the viral infection may reduce normal cilial motility. This prevents normal muco-ciliary clearance resulting in an accumulation of mucus in the sinuses and the development of the symptoms of sinusitis. If this mucus becomes secondarily infected by bacteria, acute bacterial sinusitis develops.
Read Also: What Will A Doctor Prescribe For A Sinus Infection
When Antibiotics Are Appropriate Treatment
Antibiotics may be given to people who are less able to fight off infection, such as those with diabetes, or serious heart or lung disease.
In addition, antibiotics can be given to those whose symptoms have gotten worse or those who show no improvement after seven days.
If antibiotics are given, a 10- to 14-day course is recommended, according to the practice guidelines. Amoxicillin or amoxicillin clavulanate are typically the first choice for people who are not allergic to penicillin.
Show Sources
When And Why You Might Need An Antibiotic For A Cold
Daniel More, MD, is a board-certified allergist and clinical immunologist with a background in internal medicine.
Steve Prezant / Getty
Any given adult will get a cold at least a couple of times a yearusually in the fall and winter. Kids can get many colds, maybe even half a dozen or more a year. When you get a cold, also known as an upper respiratory tract infection, should you visit your healthcare provider and get antibiotics?
The truth is, antibiotics for respiratory infections arent going to make you feel better sooner, and they might even leave you with side effects that make you feel worse.
Colds are known medically as upper respiratory tract infections because theyre usually limited to the upper half of your respiratory systemthe nose, sinuses, upper throat, larynx, and pharynx. These infections dont, for example, include infections that affect your lungs, like pneumonia.
Upper respiratory tract infections are usually caused by viruses, like rhinovirus, coronavirus, or influenza, though rarely they are caused by bacteria. Bacteria that infect the upper respiratory tract are most often S. pyogenes , or sometimes H influenzae.
Due to the development and routine administration of the H. influenzae vaccine over the past 30 years, the incidence of this infection has dropped substantially.
Antibiotics may be prescribed in a few different situations:
Also Check: Sinus Infection Turn Into Meningitis
Important Factors To Keep In Mind
- Avoid drinking alcohol and caffeinated drinks while you are on prescribed antibiotics or any sort of medicine, as alcohol intake reduces its effectiveness which makes the entire course useless.
- While other medicines are available over-the-counter, it is much better to ask your doctor first if you have certain allergies or condition. This is to avoid unpleasant reactions because a medicines effectiveness also depends on the individuals health.
- For a maximum result, never miss your dose on a given time. Make sure you check the labels and that you fully understand the instructions, particularly on the amount of dose that you are supposed to take.
- If you suddenly feel that theres something wrong in your body after taking your meds, observe how it affects you. If you show severe symptoms that you are not familiar with, do not hesitate to consult your doctor.
- Some antibiotics or medicines are not to be taken by pregnant women doctors usually recommend a certain brand for these kinds of patients.
- Maya International Bio Ampixilina
- Vicks DayQuil Cough Cold and Flu Relief
- Our rating
- XLEAR Natural Saline Nasal Spray
- Our rating
Case & Commentary: Part 2

Shortly after starting her second course of antibiotics, the patient began feeling unwell. A few days later, she was found down in her home by her daughter. The patient was brought to the emergency department for evaluation. Her work up revealed profound anemia due to brisk autoimmune hemolysis. This was thought to be due to the amoxicillin-clavulanate she had received. She was started on high-dose immunosuppressive therapy with steroids.
The chief population-level effect of antibiotic overuse is the widespread and growing problem of antimicrobial resistance . AMR is a worsening problem among many bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Escherichia coliorganisms that cause common clinical syndromes such as cellulitis, community-acquired pneumonia, and urinary tract infection. Once confined to hospitals, these drug-resistant pathogens are becoming increasingly prevalent in the community setting, and some data indicate that prior treatment with antibiotics may increase an individual patient’s likelihood of contracting an infection with a drug-resistant bacteria. AMR exerts significant societal costs, as infections with drug-resistant bacteria are associated with increased morbidity, mortality, and health care expenditures.
Don’t Miss: Best Medicine For Sinus Congestion And Sneezing
Can Sinus Infections Or Sinusitis Be Prevented
Currently, there are no vaccines designed specifically against infectious sinusitis or sinus infections. However, there are vaccines against viruses and bacteria that may cause some infectious sinusitis. Vaccination against pathogens known to cause infectious sinusitis may indirectly reduce or prevent the chance of getting the disease however, no specific studies support this assumption. Fungal vaccines against sinusitis are not available, currently.
If you are prone to recurrent bouts of a “yearly sinus infection” it may be important to consider allergy testing to see if this is the underlying cause of the recurring problem. Treatment of the allergy may prevent secondary bacterial sinus infections. In addition, sinus infections may be due to other problems such as nasal polyps, tumors, or diseases that obstruct normal mucus flow. Treatment of these underlying causes may prevent recurrent sinus infections.
Case & Commentary: Part 1
A healthy 53-year-old woman presented to her primary care physician with upper respiratory symptoms and possible sinusitis. She was prescribed Augmentin . Despite this therapy, her symptoms persisted. She was then prescribed azithromycin.
Upper respiratory tract infection symptoms are among the most common presenting complaints to primary care physicians, with 83.1 million visits occurring in 2002 , of which 3.1 million were ultimately ascribed to acute sinusitis in adults. Sinusitis occurs after or in conjunction with a viral URI. Inflammation of the respiratory epithelium lining the paranasal sinuses leads to obstruction of the sinus ostia and accumulation of mucus within the sinuses. The adjacent nasal mucosa is invariably inflamed as well. This process leads to the typical sinus symptoms of headache, nasal congestion and discharge, and facial pain or pressure, sometimes accompanied by sneezing, toothache, or fever.
Maxillary pain or tenderness in the face or teeth.
Mucopurulent nasal discharge.
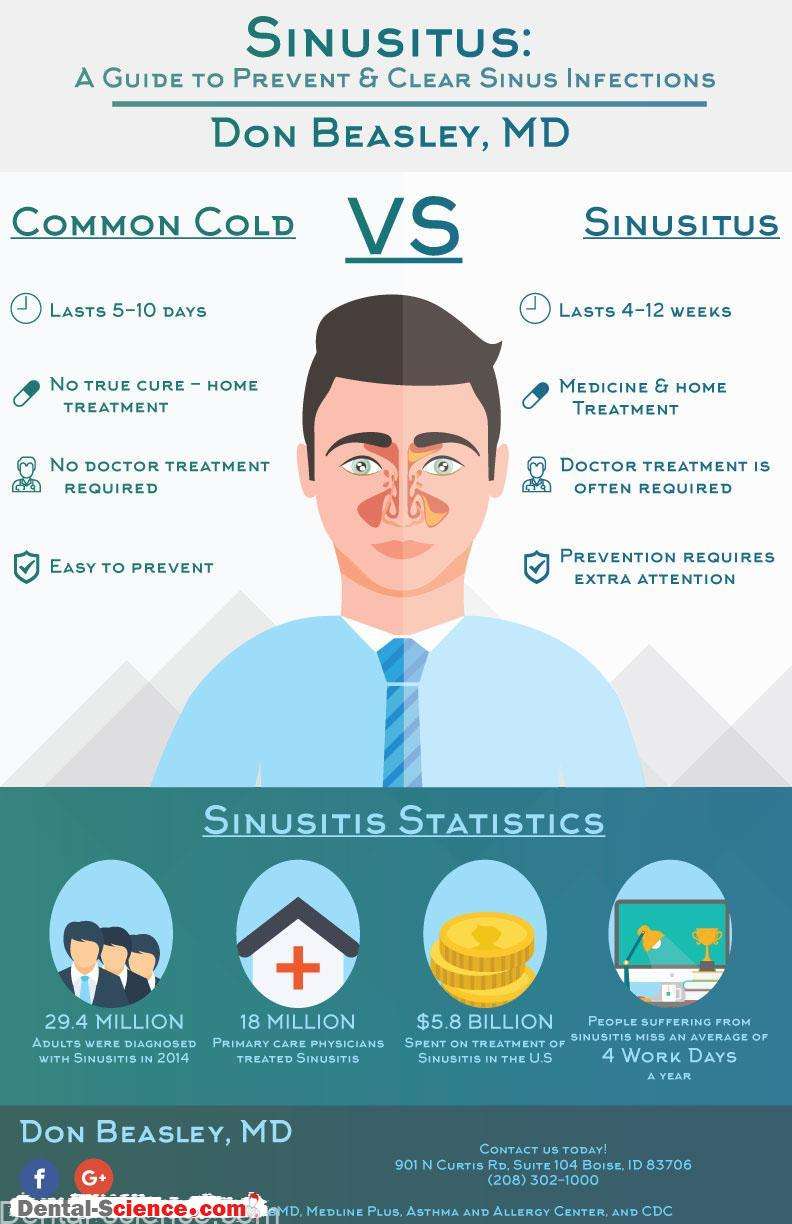
Symptoms have lasted for 7 days or more.
Despite these guidelines, overtreatment of acute sinusitis with antibiotics is common. A 2007 study found that antibiotics were prescribed in 82.7% of outpatient visits due to acute sinusitis. Many of these prescriptions are unnecessary, as the vast majority of cases of sinusitis are viral in originespecially when symptoms have lasted for less than 1 week.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Dosage For Advil Cold And Sinus
What Is A Sinus Infection
The sinuses are cavities in the head that are filled with air. These air-filled pockets are lined with a very thin layer of mucus that functions to collect particles from the air that are breathed in, such as dust, germs, or other particles.
Very small hair-like projections function to sweep the mucus, along with any particles trapped inside of the mucus. The germ- or dirt-filled mucus then slides down the back of the throat and into the stomach where stomach acid works to kill any germs.
When a sinus infection occurs, this natural process involving mucus flow is blocked.
Other Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
There are a few other reasons you might be prescribed antibiotics for an upper respiratory infection. Strep throat, medically known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a sore throat caused by infection by streptococcal bacteria. It is usually treated with penicillin.
Swelling of the epiglottis, the flap of tissue covering the windpipe, is potentially life-threatening, particularly in children ages 2 to 5 years. Called epiglottitis, this condition can impact breathing and is often caused by infection with the bacteria Haemophilus influenzae type b and should be treated with antibiotics, including a cephalosporin.
If the cold leads to an ear infection, antibiotics may help resolve it if pain relievers and decongestants dont do the trick. Antibiotic use guidelines for children with ear infections differ based on their age and symptoms.
You May Like: Over The Counter Advil Cold And Sinus
How Do You Know If Sinusitis Is Bacterial
What About A Ct Scan
A CT scan is a series of X-rays. It gives your doctor a picture of your sinuses. Some doctors recommend a CT scan when you have a sinus problem. But usually you do not need a CT scan. Generally, you only need a CT scan if you have sinus problems often, or if you are thinking about having sinus surgery.
This report is for you to use when talking with your healthcare provider. It is not a substitute for medical advice and treatment. Use of this report is at your own risk.
04/2012
Recommended Reading: Do Your Teeth Hurt With Sinus Infection
Sinus Infection Definition And Facts
- Sinusitis or sinus infection is inflammation of the air cavities within the passages of the nose.
- Sinusitis can be caused by infection, allergies, and chemical or particulate irritation of the sinuses.
- The fastest way to get rid of a sinus infection can include medications, home remedies, alternative therapies, and surgery.
- Most people do not spread sinus infections to other people.
- Sinusitis may be classified as acute sinus infection, subacute sinus infection, chronic sinus infection, infected sinusitis, and noninfectious sinusitis.
- Sinusitis signs and symptoms include
What Are The 3 Most Common Organisms Responsible For Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Abrs
For instance, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, the primary bacteria causing ABRS, are present in the body. In some cases, odontogenic sources may possess microaerophilic bacteria, and if they have microaerophilic bacteria, it is frequently identified as a odontogenic form.
Read Also: Can You Flush Out A Sinus Infection
Most Sinus Infections Dont Require Antibiotics
Ah, . The New England Journal of Medicine published a clinical practice review of acute sinus infections in adults, that is, sinus infections of up to four weeks. The need for an updated review was likely spurred by the disconcerting fact that while the vast majority of acute sinus infections will improve or even clear on their own without antibiotics within one to two weeks, most end up being treated with antibiotics.
It is this discrepancy that has clinical researchers and public health folks jumping up and down in alarm, because more unnecessary prescriptions for antibiotics mean more side effects and higher bacterial resistance rates. But on the other hand, while 85% of sinus infections improve or clear on their own, theres the 15% that do not. Potential complications are rare, but serious, and include brain infections, even abscesses.