How Does Amoxicillin Work
After starting therapy, amoxicillin will begin to work faster than many other antibiotics since it is âbactericidalâ, which means it kills bacteria. This is in contrast to âbacteriostaticâ antibiotics, which slow the growth and reproduction of bacteria but donât kill them directly.
Specifically, amoxicillin works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to what is known as penicillin-binding proteins . These are located inside the bacterial cell wall.
Amoxicillinâs ability to interfere with PBPs in the cell wall ultimately leads to cell lysis .
What About A Ct Scan
A CT scan is a series of X-rays. It gives your doctor a picture of your sinuses. Some doctors recommend a CT scan when you have a sinus problem. But usually you do not need a CT scan. Generally, you only need a CT scan if you have sinus problems often, or if you are thinking about having sinus surgery.
This report is for you to use when talking with your healthcare provider. It is not a substitute for medical advice and treatment. Use of this report is at your own risk.
04/2012
What Are The Six Types Of Sinusitis And Sinus Infections
Sinusitis may be classified in several ways, based on its duration and the type of inflammation . The term rhinosinusitis is used to imply that both the nose and sinuses are involved and is becoming the preferred term over sinusitis.
- Acute sinus infection usually lasts less than 3-5 days.
- Subacute sinus infection lasts one to three months.
- Chronic sinus infection is greater than three months. Chronic sinusitis may be further sub-classified into chronic sinusitis with or without nasal polyps, or allergic fungal sinusitis.
- Recurrent sinusitis has several sinusitis attacks every year.
There is no medical consensus on the above time periods.
- Infected sinusitis usually is caused by an uncomplicated virus infection. Less frequently, bacterial growth causes sinus infection and fungal sinus infection is very infrequent. Subacute and chronic forms of a sinus infection usually are the result of incomplete treatment of an acute sinus infection.
- Noninfectious sinusitis is caused by irritants and allergic conditions and follows the same general timeline for acute, subacute, and chronic as infectious sinusitis.
Also Check: Sore Throat And Sinus Pressure
How To Treat Sinus Infections Without Antibiotics
While sinus infections caused by viruses, allergies, or other non-bacterial factors may not require antibiotics, they still cause the same symptoms which make you feel sick.
Symptoms of a sinus infection include:
- Nasal congestion
- Pain or tenderness around the eyes, cheeks, or forehead
- Thick nasal or post-nasal drainage
Taking steps to alleviate your sinusitis symptoms is often the best treatment to lessen your discomfort.
Sinus infection treatment options include:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Rest, especially the first few days, to help your body fight the infection
- Moisturize the air with a cool-mist vaporizer
- Elevate your head while sleeping to decrease post-nasal drip
- Take warm showers or baths, as steam can soothe your sore throat and loosen mucus
- Gargle with warm salt water for a sore throat
- Use saline nasal spray or nasal irrigation kit to alleviate congestion
- Use over-the-counter treatments, such as nasal drops and sprays or pseudoephedrine pills, as your doctor recommends them
What Not to Do for a Sinus Infection
You should always follow your doctors instructions when you are diagnosed with a sinus infection.
Do not:
- Ask for antibiotics if your doctor feels they are unnecessary
- Take antibiotics that are prescribed for someone else
- Skip doses of your antibiotics or stop taking your antibiotics early when your doctor prescribes them
- Save antibiotics for the next time you get sick
Case & Commentary: Part 3

The patient’s hospital course was marked by multiorgan failure, septic shock, and spontaneous bowel perforation requiring hemicolectomy. Examination of the bowel showed Aspergillus, leading to a diagnosis of disseminated aspergillosis. Despite aggressive antifungal therapy, the patient ultimately succumbed to overwhelming infection and died.
This patient suffered a tragic outcome likely related to inappropriate prescribing of antibiotics. While the complications and ultimate outcome of this case are exceedingly rare, unfortunately, the problem of inappropriate antibiotic prescribing remains common. Over the past decade, antibiotic prescribing for ARIs has decreased in response to publicity and education regarding antimicrobial resistance. However, prescribing rates for viral infections remain high: in 2002, nearly half of adults with nonspecific ARIs were still prescribed antibiotics. Limited success in reducing overall antibiotic prescribing may be counteracted by a marked increase in prescribing of broad-spectrum antibiotics, the use of which doubled during the 1990s.
Don’t Miss: Sinus Pressure Without Nasal Congestion
Potential Side Effects Of Cephalexin
Cephalexin can be an effective way to resolve a tooth infection. But, like any medication, it can result in unwanted side effects.
Possible side effects of cephalexin may include:
- Joint pain
- Confusion
While theres no need to adhere to a special diet for cephalexin, you may want to adjust your food routine if you experience stomach problems while taking this medication.
Yogurt and other probiotic-rich foods may help soothe antibiotic-related GI troubles.If youre taking cephalexin, avoid drinking alcohol.
Alcohol can increase side effects of this antibiotic medication, including nausea, drowsiness, and dizziness.
Case & Commentary: Part 2
Shortly after starting her second course of antibiotics, the patient began feeling unwell. A few days later, she was found down in her home by her daughter. The patient was brought to the emergency department for evaluation. Her work up revealed profound anemia due to brisk autoimmune hemolysis. This was thought to be due to the amoxicillin-clavulanate she had received. She was started on high-dose immunosuppressive therapy with steroids.
The chief population-level effect of antibiotic overuse is the widespread and growing problem of antimicrobial resistance . AMR is a worsening problem among many bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Escherichia coliorganisms that cause common clinical syndromes such as cellulitis, community-acquired pneumonia, and urinary tract infection. Once confined to hospitals, these drug-resistant pathogens are becoming increasingly prevalent in the community setting, and some data indicate that prior treatment with antibiotics may increase an individual patient’s likelihood of contracting an infection with a drug-resistant bacteria. AMR exerts significant societal costs, as infections with drug-resistant bacteria are associated with increased morbidity, mortality, and health care expenditures.
Don’t Miss: Techniques To Relieve Sinus Pressure
Amoxicillin For Sinus Infection Is It Good
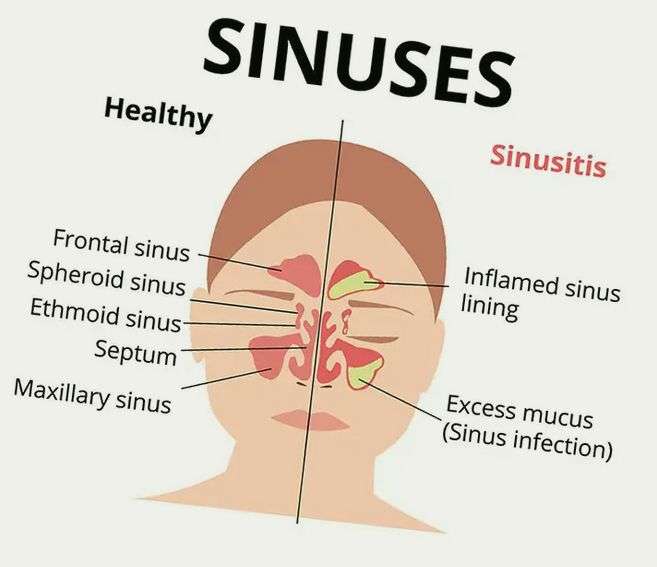
Sinus infection or sinusitis is a condition when the mucous membranes are irritated and inflamed due to bacterial, viral or fungal infection. The sinuses are air-filled connected cavities in the skull that produce a thin layer of mucus and drain into the nose.
The function of these connected systems of hollow cavities is not very clear, but experts believe that they are meant for humidifying the air and enhancing our voices.
A sinus infection may also occur when the draining mucus is blocked due to a deviated septum, nasal polyps, allergic rhinitis or common cold. Most often, sinus infection is mistaken for a common cold. Sometimes, it may be really difficult to differentiate between a sinus infection and the common cold.
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Moraxella catarrhalis are the five most common variants of bacteria that trigger sinusitis.
Streptococcal bacteria in sinuses. 3D illustration.
Amoxicillin is the first choice when it comes to treating a sinus infection as it is one of those drugs that is quite effective against combating all the aforementioned strains. It also comes with fewer side effects, when compared to other antibiotic drugs.
When Do You Really Need Antibiotics For That Sinus Infection
- By Monique Tello, MD, MPH, Contributor
It was February, and clinic was teeming with respiratory infections of all kinds: mostly the common cold, but also bronchitis, pneumonia, and sinus infections. The patients were coming in usually thinking that they needed antibiotics for their sinus infection, or another respiratory infection.The first patient on my schedule was a healthcare provider with sinus infection written down as her main issue.* Shed had about two weeks of nasal and sinus congestion which she blamed on a viral upper respiratory infection . Her two young kids had been sick with colds all winter, so she wasnt surprised to have these symptoms, along with endless postnasal drip and a cough.
Her congestion had improved a bit at one point, and she thought that she was finally getting better. But then, the day before her appointment, she awoke with throbbing pain between her eyes, completely blocked nasal passages, and, more concerning to her, green pus oozing from her left tear duct. She had body aches, chills, and extreme fatigue. Do I maybe need antibiotics? she asked.
Don’t Miss: Sinus Pressure And Blurry Vision
Treatments For Sinus Infections Other Than Antibiotics
#1: Saline Nasal Wash
Saline nasal wash can be a great way to thin out the mucous in the sinuses enough to clear out the blockage. I recommend starting this early on in the course of the illness to prevent the infection from worsening.
You can even make this at home using 2 cups of water and a 1/2 teaspoon of salt. I would add a 1/2 to 1 teaspoon of baking soda to prevent burning that can occur with use. There are also plenty of over the counter saline nasal sprays that you can purchase. You can use this 4-6 times per day.
#2: Vaporizer
Vaporizers are great because they can also thin out the mucous and make you feel a lot better. An easy home remedy, steam is probably the best way to use this treatment. Beware if you are an asthmatic as the steam could cause worsening of the asthma symptoms.
#3: Steroid Nasal Spray
Steroid nasal sprays such as Flonase have been my go to remedy recently and the great news is that they are now over the counter. The general recommendation is to use 1-2 sprays per nostril daily.
But I have found great relief using 2 sprays in each nostril twice daily. At these higher doses it is important to remember that you should use this short term, no more than 5-7 days.
These medications can significantly reduce inflammation allowing the congestion blockage to clear and significantly alleviate symptoms.
#4: Decongestants
#5: Guaifenesin
Guaifenesin such as Mucinex can certainly break up the mucous, allowing the congestion to clear more quickly.
What Are Complications Of A Sinus Infection Or Sinusitis
While serious complications do not occur frequently, it is possible for a sinus infection to cause a direct extension of infection into the brain through a sinus wall, creating a life-threatening emergency .
In addition, other adjacent structures can become infected and develop problems, such as osteomyelitis of bones in the skull and infection around the eye . Rarely, these infections may cause death. The most susceptible individuals to complications are patients with suppressed immune systems, diabetes, and relatively rarely from multiple trauma injuries that may occur in natural disasters.
Also Check: Why Do I Keep Getting Sinus Headaches
Using The Right Water During Saline Rinses
When using saline nasal rinses, tap water should always be boiled and then allowed to cool to ensure cleanliness distilled water or premixed solutions could also be used instead of regular tap water.
Other home remedies for sinus infections include:
- Drinking fluids: Drinking lots of fluids helps loosen and thin mucus. Avoid beverages that are caffeinated and alcoholic beverages that can dehydrate the body, which could thicken mucus.
- Breathing steam: Warm water is best . You can breathe in steam from either a bowl or shower.
- Humidifying the air: Use a cool air vaporizer or humidifier,particularly at night while sleeping.
- Avoiding environmental substances: Avoid tobacco smoke and chlorinated water that can dry up the mucus membranes and exacerbate symptoms.
- Implementing treatment measures: At the first sign of infection, use antihistamines and employ regular nasal rinses.
Which Types Of Doctors Treat Sinusitis And Sinus Infections
- Many sinus infections can be treated by your primary care physician or an Internal Medicine doctor.
- However, it is not unusual to consult an ENT specialist, infectious disease specialist, or an allergist or immunologist.
- With some complex sinus infections, a surgeon who specializes in sinus surgery may be necessary to consult.
Don’t Miss: Does Guaifenesin Help With Sinus Congestion
Which Disorder Causes A Foul Smelling Nasal Discharge
Sinusitis, more commonly known as a sinus infection, affects around 31 million people in the U.S. Symptoms include pain and pressure in sinus cavities, congestion, headache, bad breath and loss of smell. As mucus drains from the sinuses into the nasal cavities and throat, you may experience a bad smell.
Read Also: What Antibiotics Treat Uti And Kidney Infections
Viral Vs Bacterial Sinus Infections
Most sinus infections are caused by viruses that create inflammation in the sinuses, leading to blockage that can make it hard to breathe, nasal secretions, postnasal drip, and other discomfort like facial pain around your eyes, cheeks, nose, or forehead.
Knowing thisand that antibiotics dont work on viral infectionsmost healthcare providers first recommend treatments to relieve the symptoms of a sinus infection while you wait for it to resolve.
These may include:
- Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to ease discomfort from swelling, fever, or sore throat
In rare cases, viral sinus infections can lead to bacterial growth in the nasal passages.
Theres no way to know for sure if you have a bacterial sinus infection without testing a mucus sample.
But even without a sample, two signs typically indicate a bacterial infection and may prompt your provider to prescribe antibiotics:
- A sinus infection that lasts for more than 10 days
- Symptoms of the infection resolve, then back worse a couple days later
Some people think yellow or green mucus may be a sign of a bacterial sinus infection, but colored mucus can occur with viral infections and does not necessarily mean you have a bacterial infection.
If you do have bacterial sinusitis , it should respond to antibiotics within a few days.
Recommended Reading: Sinus Infection How To Treat At Home
Why Is Cephalexin More Effective
Bacteria tend to develop quick resistance against these beta-lactam drugs. They do so by secreting an enzyme known as beta-lactamase. This enzyme retards the activity of drugs similar to Cephalexin. However, experiments on a large number of patients have shown that very low resistance is developed against Cephalexin. This attributes to the high efficiency of Cephalexin in treating the sinus infection.
When Do We Need Antibiotics For Sinus Infection
Antibiotics are not needed for many sinus infections, but your doctor can decide if you need an antibiotic. You doctor may recommend antibiotics if:
Most sinus infections usually get better on their own without antibiotics. When antibiotics arent needed, they wont help you, and their side effects could still cause harm. Side effects can range from minor issues, like a rash, to very serious health problems, such as antibiotic-resistant infections and C. diff infection, which causes diarrhea that can lead to severe colon damage and death.
Read Also: Saline Solution For Sinus Pressure
Recommended Reading: How To Break Up Severe Sinus Congestion
Skipping Or Overdose Of Augmentin For Sinus Infection
If you have missed a dose of Augmentin, if theres enough time between the skipped dose and the next dose, then take it. Otherwise, if the next dose is near, skip the missed dose and stick to your regular schedule.
In case the patient takes an overdose accidentally and he/she is experiencing symptoms such as stomach pain, diarrhea, frequent urge to urinate, drowsiness or cloudy urine, then take them to to the doctor without further delay.
Types Of Sinus Infections: Chronic Vs Acute
There are four types of sinus infections. These classifications depend on the length and frequency of the infection:
- Acute sinusitis.This type of sinus infection lasts only for a short time, defined by the American Academy of Otolaryngology as less than 4 weeks. This short-term infection is usually part of a cold or other respiratory illness. It may also be caused by a bacterial infection .
- Subacute sinusitis. A subacute sinus infection lasts between 4 and 12 weeks .
- Recurrent acute sinusitis. An acute sinus infection is considered recurrent if the infection returns four or more times within a year, with each infection lasting 7 days or more.
- Chronic sinusitis.Chronic sinus infections last for more than 12 weeks or continue to recur.
Many sinus infection symptoms are common in both acute and chronic forms. Seeing a doctor is the best way to learn if you have an infection, find the cause, and get treatment.
For cases of acute bacterial sinus infections, these symptoms last at least 10 days without improving, or they worsen within 10 days after seeming to improve. In this case, its important to talk with a doctor, such as a general practitioner or an ear, nose, and throat doctor , to get a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Learn more about the symptoms of a sinus infection below.
Dont Miss:
Also Check: Tension Headache Or Sinus Headache
Interactions Of Amoxicillin For Sinusitis
As the Amoxicillin 500 mg Tablet is allopathic medicine, it can easily react with other medicines that you are taking. The other medicines, when combined with Amoxicillin 500 mg tablet, can worsen the side effects of Amoxicillin 500 mg Tablet.
Not only the side effects but any underlying health issue can also aggravate if this medicine is taken without the doctors approval.
Medicines that can interfere with Amoxicillin 500 mg Tablet and can cause moderate or serious side effects are-
- Allopurinol
Know here:Best sinus medicines to take
What You Should Not Do To Soothe A Cold Or Ear Infection:
- Do not give over-the-counter cold medicines to children under age 2. Consider avoiding them if the child is older, too.
- Do not tilt an infants crib mattress. Children under age 1 should sleep on a flat mattress with no pillows or blankets.
- Do not allow a child to drink while lying down, as it can increase the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Do not smoke. Families and caregivers who smoke increase a childs chance of getting colds and ear infections.
Because young children get more colds in the winter, they may also develop more ear infections. Five out of six children will experience at least one ear infection by the time they are 3 years old, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Don’t Miss: Sinus Infection Not Getting Better