Why Might Your Doctor Recommend Antibiotics For Sinusitis
You doctor may recommend antibiotics if:
- You have symptoms of a bacterial infection and you have not gotten better after 10 days, even with home treatment.
- Your symptoms are severe, or you have other problems, such as pus forming in your sinus cavities.
- You have had sinusitis for 12 weeks or longer .
How To Treat A Sinus Infection At Home
In the first two weeks of a sinus infection, patients may use saline sprays, over-the-counter steroid sprays like Flonase, and over-the-counter decongestants.
After 10 days, if the drainage is still colored, an antibiotic is likely necessary. Theres no homeopathic alternative to antibiotics. However, saline spray, topical steroid sprays, and decongestants work well with antibiotics to clear most infections.
World Breastfeeding Week August 1
This year, WABAs emphasis for World Breastfeeding Week is on strengthening the capacity of actors that protect, promote and support breastfeeding across different levels of society including governments, health systems, workplaces and communities to provide and sustain breastfeeding-friendly environments for families in the post-pandemic world. According to WABA, breastfeeding can assist with sustainable development strategies post-pandemic, as it can improve nutrition, ensure food security, and reduce inequalities between and within countries.
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Sinus Drip
The Symptoms Of A Sinus Infection
People often assume that its possible to tell the difference between a viral and bacterial sinus infection based on the type of symptoms they experience. Unfortunately, thats not the case. Usually, the symptoms of a sinus infection are the same or very similar whether its caused by bacteria or a virus.
Common symptoms of either a viral or bacterial sinus infection include green or yellow mucous/discharge, bad breath, headache, and fever.
Lingering Sinus Infection Or Chronic Runny Nose
A lingering sinus infection is different from a chronic runny nose. Chronic runny nose typically comes from allergies or other irritants in the air. However, this can turn into an infection over time.
When the sinuses become infected, the allergies, irritants, or viral cold have caused swelling in the nose thats blocked the drainage pathways. Consequently, fluid and mucous accumulate in the sinuses, where it has become infected with bacteria.
If youve been sick more than 10 days and begin to experience other symptoms like facial pressure, headache, and fever, youre dealing with more than a chronic runny nose.
You May Like: How To Relieve Sinus Pressure With Fingers
Signs And Symptoms Of Sinusitis:
A case of acute sinusitis presents with the following signs and symptoms:
- Facial pain and tenderness on pressure
- Nasal congestion
By Jessi Cole, January 2, 2019
Winter is a season for sinusitis and sinus infections, and that often means lost productivity, as workers either call in sick or try to power through. Its difficult to be at your best when youre suffering from the symptoms of a sinus infection, and your productivity will almost always take a hit as a result. But is it necessary to call out of work, for the sake of your own health as well as that of others?
Recommended Reading: Does A Sinus Infection Heal On Its Own
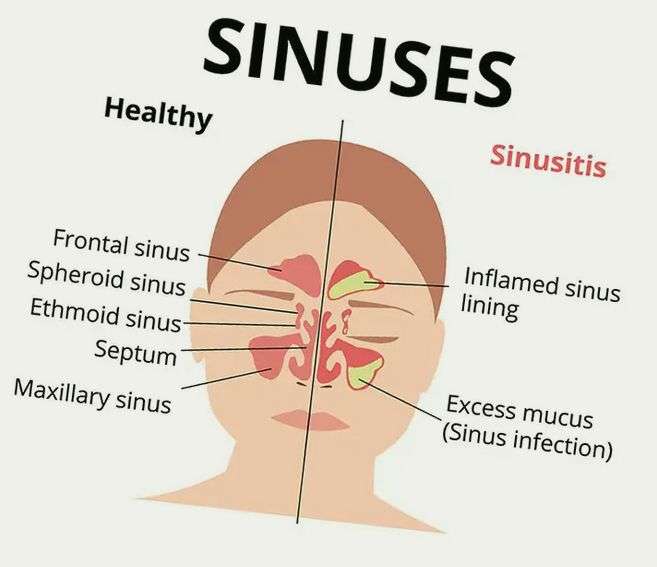
What Are The Sinuses How Many Do We Have
A sinus is a hollow, air-filled cavity. For the purposes of this article, a sinus will refer to those hollow cavities that are in the skull and connected to the nasal airway by a narrow hole in the bone . Normally all sinuses are open to the nasal airway through an ostium. Humans have four pair of these cavities each referred to as the:
The four pairs of sinuses are often described as a unit and termed the paranasal sinuses. The cells of the inner lining of each sinus are mucus-secreting cells, epithelial cells, and some cells that are part of the immune system .
Functions of the sinuses include humidifying and warming inspired air, insulation of surrounding structures , increasing voice resonance, and as buffers against facial trauma. The sinuses decrease the weight of the skull. If the inflammation hinders the clearance of mucous or blocks the natural ostium, the inflammation may progress into a bacterial infection.
Read Also: Does Any Antibiotic Cure Chlamydia
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Sinus Headache From Allergies
Ways To Recognize Serious Signs Of Sinus Infections
#1: Duration
The length of the infection is an important determinant of the seriousness of the infection.
I usually consider most infections less than 3 weeks to be viral or inflammation related to congestion. At this point, the best treatment is usually medications that decrease the congestion and inflammation. This in turn will alleviate the symptoms and ultimately cure the illness.
When the illness continues beyond 3 weeks, bacterial infection can begin to develop. Though antibiotics can be considered at this point, other treatments may still be the best answer if they have not yet been given a try.
#2: Mucous Color
I will dispel a myth right here and now. Yellowish/greenish mucous does not necessarily mean the infection is bacterial.
Viruses can cause the same color mucous. The reason for the mucous is generally not the actual bacteria or virus, but the bodys immune response to the intruder.
So dont worry just because you see a colored mucous when you blow your nose. This will also improve as the infection abates.
#3: Sinus Pain
Sinus pain can occur anytime throughout a sinus infection. This is normal and means there is inflammation in the sinuses, as we discussed previously.
However, severe pain, redness over the skin, hardened skin over the sinuses, or even a severe headache are not generally normal and can indicate a bacterial infection.
#4: Fever
A fever can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. So how do you differentiate between the two?
Runny Nose And Postnasal Drip
When you have a sinus infection, you may need to blow your nose often because of nasal discharge, which can be cloudy, green, or yellow. This discharge comes from your infected sinuses and drains into your nasal passages.
The discharge may also bypass your nose and drain down the back of your throat. You may feel a tickle, an itch, or even a sore throat.
This is called postnasal drip, and it may cause you to cough at night when youre lying down to sleep, and in the morning after getting up. It may also cause your voice to sound hoarse.
Dont Miss: Antibiotics Used For Yeast Infection
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get S Sinus Infection
Sinus Infections That Dont Quit: When You Should Worry
Coconut oil can be used in a variety of ways to treat sinus infections. Adding a tablespoon to tea or coffee and drinking it is one method. Likewise, the oil can be swished in the mouth and spat back out using an oil pulling method. Finally, the oil can also be used as a nasal rinse by using a dropper or neti pot This is why its important to understand the best way to stop a sinus infection and relieve post nasal drip. How do you stop a sinus infection? If your sinus infection and post nasal drip with cough lasts between 7-10 days, you should be okay handling things at home on your own Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis is an infection of both your nasal cavity and sinuses. It is caused by bacteria. The nasal cavity is the large air-filled space behind your nose. The sinuses are a group of spaces formed by the bones of your face. They connect with your nasal cavity The swelling can commonly last a couple of weeks. If the tube stays completely swollen for more than a couple of days, you could even begin to build up fluid behind the eardrum. In addition to colds, nasal allergies, sinus infections and even stomach acid reflux can cause the Eustachian tube swelling A bad cold is often mistaken for a sinus infection. Many symptoms are the same, including headache or facial pain, runny nose and nasal congestion. Unlike a cold, a. sinus infection symptoms may be caused by bacterial infections. It often requires treatment with antibiotics
What Are The Different Types Of Sinus Infections
Most sinus infections are caused by viruses, and theyll usually go away on their own. In fact, if the infection doesnt clear up after a week to 10 days, it can be an indication that its caused by bacteria. It may have started as a bacterial infection, or a viral infection may develop into a bacterial infection after your sinuses become filled with fluid and bacteria then forms.
If you have sinus infections that seem to clear up only to shortly return, you probably have a bacterial infection. Thick, dark, or greenish-yellow nasal discharge is another indication, but your doctor can perform tests to verify the type of infection if needed.
Sinus infections can also be classified as acute or chronic. Acute infections usually start suddenly with symptoms such as a runny, stuffy nose and facial pain and can last up to four weeks. Chronic sinusitis occurs when your infection persists for at least 12 weeks despite attempts to treat it.
In the short term, a sinus infection can cause a long list of symptoms, including the following:
Read Also: How Long After Taking Antibiotics Will My Tooth Stop Hurting
Also Check: New York Allergy Asthma And Sinus Center
Aromatherapy Humidity Nasal Sprays & Steam
The tried and true remedy of using a humidifier or a steamy shower can also help provide temporary relief from sinusitis symptoms such as sore throat. Essential oils such as peppermint or eucalyptus may also help to open up your sinuses and relieve some of the blockage thats indirectly causing your sore throat. Finally, flushing out your mucus with a neti pot or a saline nasal spray can also provide temporary relief.
Is 5 Days Of Antibiotics Enough For Sinus Infection
When antibiotics are prescribed for sinus infections, only five to seven days of therapy are needed for uncomplicated cases, when patients start to recover within a few days of starting treatment and if they dont have signs that the infection has spread beyond the sinuses, according to the Infectious Diseases Society
You May Like: Can Antibiotics Cure A Kidney Infection
Read Also: Best Medicine For Runny Nose And Sinus Pressure
Common Antibiotics For Sinus Infections
Antibiotics may be prescribed when symptoms of a sinus infection warrant such treatment. Common antibiotics for sinus infection include:
- Levaquin : Although this drug is sometimes prescribed as a first line of therapy for sinusitis, it has serious side effects and should only be used as a last resort.
Most Common Antibiotics Used For Sinusitis
The most commonly recommended antibiotic for acute, uncomplicated bacterial sinusitis is amoxicillin.
Its most effective when the patient takes it frequently enough to maintain adequate levels in the infected tissue. Often, doctors prescribe it twice daily, though three or four divided doses can be even more effective. Amoxicillin is usually prescribed for seven to ten days. While it is crucial to finish the entire ten-day course of antibiotics for strep throat, shorter courses could be sufficient for several cases of sinusitis.
Azithromycin is an alternate treatment option for those who are allergic to amoxicillin. The primary benefit of azithromycin is expediency. The suggested treatment for acute bacterial sinus infections is 500 mg once daily for three days. Unlike amoxicillin, azithromycin is even more effective when doctors prescribe a sizeable single dose instead of spreading the doses out.
Recommended Reading: Best Thing To Take For Sinus Pressure
Antibiotics And Sinus Infections
When a sinus infection hits, it seems worse than what you remembered from the last time you had one. This may give you the idea that you need antibiotics, but most clear up without them. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses and aren’t recommended within the first week of developing a cold. About 70% of sinus infections go away within two weeks without antibiotics.
Consider these other forms of treatments instead of antibiotics:
- These medications are available for over-the-counter purchase. Be careful to only take these medications for a few days at most, as they can cause the return of more severe congestions.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers Aspirins, acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve temporary pain.
- Saline nasal spray This is used to spray into your nose several times a day to rinse your nasal passages. It can help to prevent and treat inflammation.
Antibiotics only will be needed if the infection is severe, recurrent or persistent.
The likelihood of bacterial infection increases when:
- Symptoms last seven days or more, particularly when symptoms initially improve and then worsen.
- Mucus is thick and yellow or green in color.
- There is facial or sinus tenderness, particularly if it’s worse on one side of the face.
- Pain is present in the upper teeth and is worse on one side of the face.
If the infection becomes severe, recurrent or persistent, contact your provider.
When To Use Antibiotics To Treat A Sinus Infection
Antibiotics only work against bacterial infections, so the best time to use them for a sinus infection is when you and your doctor suspect bacteria caused the infection.
Otherwise, you may be at risk for unwanted side effects or even antibiotic resistance.
When this happens, bacteria outsmart the medications designed to kill them, and the antibiotics no longer work when you need them.
That said, it can be hard to know whether a sinus infection is viral or bacterial.
Some scenarios, such as an infection that persists longer than 10 days or an infection that goes away and then returns, may indicate a bacterial infection and prompt a provider to prescribe antibiotics.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may also treat a sinus infection with antibiotics as a precaution to prevent complications in people with compromised immune systems that cant easily fight off infections.
If your doctor prescribes antibiotic treatment, follow their instructions.
Take the antibiotics at the same time every day. If you miss a dose, take it when you remember or, if its close to your next dose, wait until then and take one dose.
Do not double up on antibiotics doses.
If you experience unwanted side effects of antibiotics, your sinus infection isnt improving, or you develop new symptoms, contact your healthcare provider, who can help you figure out whats going on.
While sinus infections usually dont cause major medical problems, they can have severe symptoms and other complications.
You May Like: Can Sinus Cause Ringing In Ears
Do Antibiotics Treat Sinus Infections
Antibiotics are a type of medication that stops bacteria from growing and, as a result, improves symptoms of an infection.
Healthcare providers only prescribe antibiotics for sinus infections that they believe are bacterial.
Antibiotics dont work on viral or fungal infections, and taking antibiotics when you dont need them can cause unnecessary side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and stomach pain.
Plus, taking antibiotics too often can create antibiotic resistance.
The most common antibiotics prescribed for sinus infections are penicillin-class antibiotics such as amoxicillin or amoxicillin-clavulanate .
If you have a penicillin allergy, a common alternative is doxycycline.
How Is Sinus Infection Diagnosed
Diagnosis depends on symptoms and requires an examination of the throat, nose and sinuses. Your allergist will look for:
- Discolored nasal discharge
If your sinus infection lasts longer than eight weeks, or if standard antibiotic treatment is not working, a sinus CT scan may help your allergist diagnose the problem. Your allergist may examine your nose or sinus openings. The exam uses a long, thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera and a light at one end that is inserted through the nose. It is not painful. Your allergist may give you a light anesthetic nasal spray to make you more comfortable.
Mucus cultures: If your sinus infection is chronic or has not improved after several rounds of antibiotics, a mucus culture may help to determine what is causing the infection. Most mucus samples are taken from the nose. However, it is sometimes necessary to get mucus directly from the sinuses.
Knowing what kind of bacteria is causing the infection can lead to more effective antibiotic therapy. A fungus could also cause your sinus infection. Confirming the presence of fungus is important. Fungal sinus infection needs to be treated with antifungal agents, rather than antibiotics. In addition, some forms of fungal sinus infection allergic fungal sinus infection, for example do not respond to antifungal agents and often require the use of oral steroids.
Don’t Miss: Is Sinus Congestion A Sign Of Pregnancy
Caveats: Refer Seriously Ill Patients And Complicated Cases
A very important caveat to our recommendation is that seriously ill patients must be managed differently. Very infrequently a patient develops a serious complication of acute sinusitis such as brain abscess, periorbital cellulitis, or meningitis. Therefore, seriously ill patients with signs and symptoms of acute bacterial sinusitis, such as high fever, periorbital erythema or edema, severe headache, or intense facial pain must be carefully evaluated and treated with great caution and close follow-up. These patients should be referred immediately for consultation with an otolaryngologist.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection

There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
- Otitis media with effusion sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotic Ointment For Diaper Rash
Also Check: Antibiotic For Bronchitis And Sinus Infection